(�b�a�[�� = 0%�A�b���[�� = 100%)
100% �b���[������ήɶ��G
�ۥѿ�ܡA�I��H�U�a���[�ݿ줽�ɶ��Φ�m
�ҮɡG 30 �p��
�ɥήɴ��G 15 �P���C�i�ץѱz����A�i�֥i�C�C
�Ұ���v�ɮv�GLarry
�b�էK�O��ڻ�G�� 3 �p���A�ЭP�q�H�W�a�I�P������¾���w���C
���ҵ{�����b�էK�O��ڻ���ɮv�ѵ��A�ȡC
(�b�a�[�� = 100%�A�b���[�� = 0%)
100% �b�a�[������ήɶ��G
�C�� 24 �p�ɥ��ѭԤ������Ʀa�[��
�ҮɡG 30 �p��
�ɥήɴ��G 15 �P���C�i�ץѱz����A�i�֥i�C�C
�Ұ���v�ɮv�GLarry
�b�էK�O��ڻ�G�� 3 �p���A�ЭP�q�H�W�a�I�P������¾���w���C
���ҵ{�����ɮv�ѵ��A�ȡC
Fortinet �O�@�a���y����������w�����q�A�� 2000 �~���ߡCFortinet �M�`�Ѽs�x�������w���ѨM��סA�]�A������ (Firewall)�B�J�I���m�t�� (IPS)�B���r�n��B�����p�H���� (VPN)�B�H�κ����y�q�z�u��C
Fortinet�����~�M�A�Ȧ��b�O�@���~�M��´�K���U�������¯١A�p�c�N�n��B�ǯ��n��B���������M���������_�A�ȧ��� (DDoS)�C
Fortinet ���էQ�Ҧ��O�q�L�P���w��]�ơB�n��q�ΪA�ȩM�M�~�N�䴩�C��֤߲��~ FortiGate ������H���ʯ�M�������w���\�ਣ�١A�O Fortinet �b���y�����w�����������ڤF���n�a��C
���~�AFortinet �ٴ��� FortiGuard Labs ���¯ٱ����M�w���A�ȡA���Ȥᴣ�ѧY�ɪ��¯٨��m�M�w����s�C
�ھ� IDC ������s���i�AFortinet �b���y�����w���������֦���۪��������B�A�ר�O�b�Τ@�¯ٺz (UTM) �M���~��������C
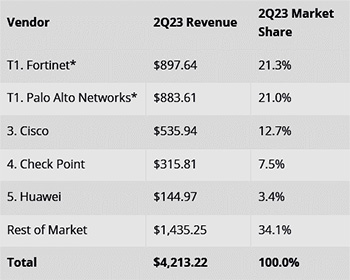
Top 5 Companies, Worldwide Security Appliance Total Market Revenue and Market Share
���M���饫�����B�ƾڥi��|�H�ɶ��ܰʡA�� Fortinet �b�o�ǻ��q�`��C�e�T�A�P��L����������w�����q�v���A�p Cisco�BCheck Point �M Palo Alto Networks�C
Fortinet �z�L���_�зs�M�X�i�䲣�~�զX�A�T�O��b���_�ܤƪ������w����줤�O������a��C
Fortinet �b���y�֦��h�Ӭ�o���ߩM��ƳB�A���ΤF�W�L 13,000 �W���u�A�O�����w����~���T�j��ɪ̤��@�A�Ԩ��H�U Gartner - Magic Quadrant for Network Firewalls:
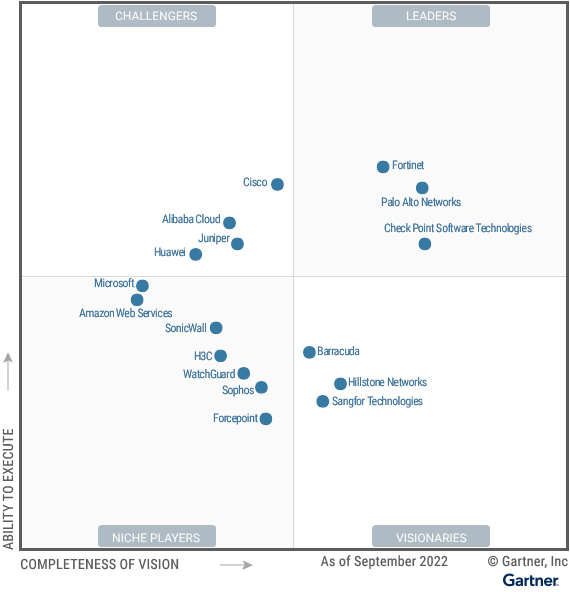
�@���@�a�P�O������w�������q�AFortinet �`�����ʺ����w�����зs�M�o�i�A�P�~����L���q�M��´�X�@�A�@�P���藍�_�X�{�������¯١C
Fortinet (NASDAQ: FTNT) �����Ȭ��� 583 ������ (�W�L4540���䤸)�A�O���y�����w����~��������~���@�C�ھڸӤ��q���~�װ]���ƾ���ܡA����~�禬�� 53 �������A���W�~�P���W�� 20%�F��Q���� 40 �������C
�`��Ө��AFortinet �b�����w����~�֦�í�����]�Ȫ��p�M�j�j�������a��A�ë���q�L�N�зs�M�~�ȩݮi�ӱ��ʨ�b���������v���O�C
Fortinet ���֤ߧN�GFortiOS (���ҵ{���D�n���e)
FortiGate Next Generation Firewall (NGFW) ���~�ĥΤF�M�Ϊ��w���B�z���� (ASIC)�A�ö����F�ۦ��� FortiGuard ����Ǫ��¯ٱ����A�ȡA���ѷ~�ɻ�����w���O�@�\��M�]�A�[�K�y�q�b�����W���ʯ�C

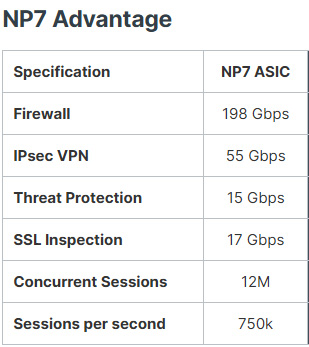
�o�DZM�Ϊ��w���B�z������ Fortinet �˦۳]�p�å�� TSMC (�x�n�q) �H����í�w�ν���u�}�� 7 �Ǧ̨�{�Ͳ��C�H NP7 ���ҡAFortinet ����@�w���B�z�������L�o�į�i���F 198 Gbps�I
FortiGate �Ҵ��Ѫ����ΡB�ϥΪ̩M������ı�Ƥj�j���C�F�]�w�κʹ�����w���������{�סA�P�ɬ��A���]�w���Ѧw�����ŤΫ�ij (Security Advise)�A���A������q�����w�����̨γ]�w (Security Best Practice)�C
�����w���u�{�v�Ҽ{���O�p��ϥ� FortiGate �����𬰨���~���ѥ������¯٨��@�A�o�]�A�J�I���m�BWeb �L�o�B�ϴc�N�n��M���ε{������C
�̾ڵۦW��s���c Gartner �����_�A80% �����~�y�q (Traffic Flow) �O�B��Q�[�K�����A�A�� 50% �w����~�������O���æb�[�K�y�q���C�]���A�{�N������w��w�[�K���y�q�B�z�B���������B�J�I���m�B�ƦܬO���_�[�K�y�q����O�Ωʯ�A�b���ɤ��骺���~��o�S�O���n�I
FortiOS �@���ߤ@�� FortiGate ������@�~�t�ΡA�N�R���o���F Fortinet �w���B�z�������ʯ�A�H��@�����C�����F 17Gbps ���ʯ�ӳB�z�ΫO�@�w�[�K���y�q�C�������������� FortiGate �������w�˦h�� NP7 �w���B�z�����H�F����[�K�y�q�B�z�ʯ�C
FortiOS �@�~�t�άO Fortinet Security Fabric ���֤�
FortiOS
�U���c�β�´�b���i�Ʀ�Ƴзs (Digital Innovation) ���L�{���A���ݭn�T�O��w���ʯ��o�W���������������U�ܪ��¯١C
�ھ� Gartner�BIDC�BForester Research �� Cisco Annual Internet Report �� 2018 �� 2023 �o���~�����A���~�ϥβݥΤ�]�ƥѬ� 30 ���W���� 50 ���A�i�Q�Ӫ�������t���w���ζլO�۷��Y�m���C
���G ������t (Edge of the Network) �q�`�O�������[�c������Τ�ݪ����@�h�A�o�ز[�\�F�ݥΤ�]�� (�p����B�q��)�B���ݤ�����c (Branch & SOHO) �������]�ơA�H�λP���p�� (IoT) �������˸m���A���~�X�{�z�����W���C
�H�ۤu�@�Ҧ������ܡA�o�Ǻ�����t�]�Ʀb�ƶq�W�A�H�Υ��̩ҥͲ��M�B�z�ƾڪ���t�W���A������ɤw���A���H�����������[�c���˲M���A�ӬO��[�����A�ɭP�F������ɪ��H���ơC�G���o�n�D�����w������������[�A���o�إh���ߤƪ��[�c�A�q�ӽT�O�Ҧ�������t���w���ʡC
�h�~�Ӭ��F�ѨM��@���D�ӲK�[�U���U�ˤ��ۤz���w�����~�A�å��Ҽ{�����w���ʭ�h�A�ɭP�X�{�U�غz�W���D�ԡC�ӧֳt�W����������t�h�[�@�F�o�ǬD�ԡC
�H���A�o�Ǥ��P���ѨM��O�L�k�ۤ���@�Τ��ɸ�T���A�ɭP�L�k�@�P�a����w���ʭ�h�M�ݨ�ݥi���ʡC�Ӻ����M�ʱ����h���V�X�B�w��B�n��M ��X-as-a-Service�� (���@���� �Y�A��) �ѨM��פ]�Ϧw���ζ��������t�C
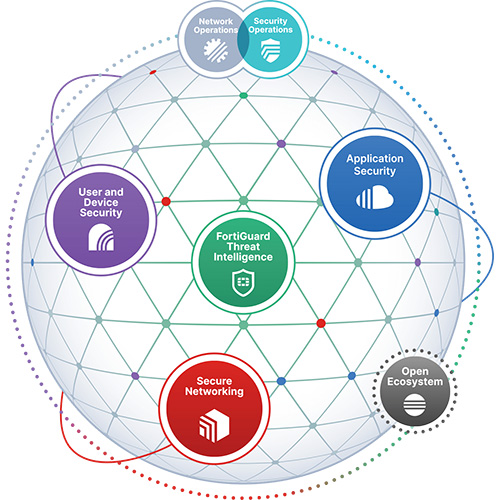
Fortinet �� FortiOS �@�~�t�άO Fortinet Security Fabric �w���ج[����ۡA��\�h�N�M�ΨҾ�X���F�Τ@�¯٨��@�ѨM��� (Unified Threat Management�AUTM)�C
���A�z�L���ҵ{�Ƿ| FortiOS UTM �ѨM��סA�A�N�|���A�����c�β�´�a�ӥH�U���n�B�G
- �F���ʩM�A���ʡG�Q���F�����ѨM��רӳB�z�{�N�]�I���U�ؽ������w���]�w�C
- ������X�M�z�G�A�i�H�N�Ҧ��\���X�b�@�Ӻz����x���i�汱��C
- �������įq�G��֤F�A���O�@�����ӧ�J���]�Ƽƶq�A��ۦa�`�٦����C
- ����������w���¯٪��{�ѡG�ϧA���ζ������n�a�z���ū���ʫ¯٩M��L�{�N�M�I�C
- ��ָ��ꪺ�w���ѨM��סG²�ƼƾڳB�z�覡�A�æP�ɨϥΧ�֪��귽�C
���F���ɧA�b�����w���譱���ޯ������ Fortinet FCA �{�Ҫ���O�A���ҵ{�N�Ժɱб� FortiOS ���\��� FortiGate �����𪺳]�w�A�Ҧp�G
- FortiGate ������t�C�ΥؼХ������z
- �]�w���P�����������d (Interface)�B������}�ഫ�N (NAT) �M���� (Routing)
- ������ (Firewall Policy)
- �����ϥΪ̨������� (User Authentication)
- �ˬd SSL/TLS �y�q
- ���״c�N�n��
- �����L�o (Web Filtering)
- �]�w FortiGate �J�I���m�t�� (IPS)
- �������ε{������ (Cloud Application Control)
- �إ� IPsec �����p�H���� (VPN)
- �]�w FortiGate SSL VPN
- FortiGate NGFW �t�ΤɯšB���@�P�ʱ�
- �]�w Fortinet �w���[�c (Security Fabric)

FCA
�������ҵ{��A�A�����i�H�Ҩ� FCA �{�ҡA�A�٥i�H��Ƿ|�������w�����ѤΧN����a�ϥΩ�H�U�� FortiGate ������t�C���~�A�ç���A�����~���ҡI
Entry Level - FortiGate 40F, 50G, 60F, 70F, 80F, 90G series

Mid Range - FortiGate 100F, 120G, 200F, 400F, 600F, 900G series

Datacenter - FortiGate 1000F, 1800F, 2600F, 3000F, 3200F, 3500F, 3700F, 4200F, 4400F, 4800F, 6001F, 6300F, 6500F, 7081F, 7121F

| �ҵ{�W�١G |
Fortinet Certified Associate Cybersecurity (FCA) ��ڻ{�i�Үѽҵ{ - ²�١GFortinet FCA Training Course |
| �ҵ{�ɼơG | �X�@ 30 �p�� (�@ 10 ��) |
| �A�X�H�h�G | ��q����������¦�{�Ѫ�����H�h�C |
| �½һy���G | �H�s�F�ܬ��D�A���H�^�y |
| �ҵ{���O�G | �����߾ɮv�˦۽s�g�^�嬰�D���O�A�ӳ����^��r���������ӡC |
| 1. Larry Chan �˦۱б¡G | Larry ����Dz߸`���A�`�J�L�X�A�O�ǭ��b���P��^�U�A�x���q���ޥ��C |
| 2. Larry Chan �˦۽s�g���O�G | Larry �˦۽s�g���O�A����A�X FCA �Ҹդι�ڤu�@���ΡC |
| 3. ���Ѽ����Ҹ��D�ءG | �����߬��ǭ����� FCA �������Ҹ��D�ءA�C���Ҹ��D�ا������зǵ��סC�Ӹ����z�Ѫ��D�ءA���|���� Larry �������C |
| 4. �z�P��ߨí��G | �����ߪ� FCA �ҵ{�j�����ɶ��H��ߥܽd�Φ��б¡A�O�ǭ��u���F�Ѥδx��FortiGate������z�����n�ޥ��C |
| 5. �@�H�@���W�ҡG | ���ҵ{�H�@�H�@���Ҧ��W�ҡC |
| 6. �K�O��Ū�G | �DzνҰ�ǭ��i��ҵ{������T�Ӥ뤺�K�O���ݽҰ���v�C |
�u�n�A��U�C��ب��o�X�榨�Z�A�K�i�� Fortinet �{�o Fortinet Certified Associate Cybersecurity ��ڻ{�i�ҮѡG
|
����ئҸնO�Υ��K�AFortinet FCA �O��a�����Ҫ��D���}�Ҹլ�ءA�ӳ��ҫe�ҥͻݶi��@�ǥ� Fortinet ���w�����W�{�ǤΤ���C �����߾ɮv�N��Ұ��ѳq�L�ӵ{�ǤΤ����T���ܡA�O�A���Q���ҧK�O�ҸաC �Ҹ��D�إѦҸդ��߶ǰe��A�n���Ҫ��q���A�ҸծɥH�q���@���C�Ҧ��Ҹ��D�ا����^��A�Ӥj�h�ƪ��Ҹ��D�ج��涵����D (�N�Y O) �Φh������D (�N�Y �f)�A�H�ι���D�C�@��������|�ߧY�X�{�A�����ơA���G�Y�ҧY���I �Ҹդ��X��K�i�� 15 ��᭫�s���ҡA�������ơC�����D�@���ɶ��B�D���`�ơB�X����Ƶ��ԲӦҸո�ơA�i�s�������ߺ��� "�U��Ҹդ��Ƹ��"�C |
| �ҵ{�W�١GFortinet Certified Associate Cybersecurity (FCA) ��ڻ{�i�Үѽҵ{ - ²�١GFortinet FCA Training Course |
1. FortiOS
1.1 �V�X�������[�c������
1.1.1 �z IT ������
1.1.2 �����w���ޯศ�t
1.1.3 �i���¯ٿ��_
1.1.4 AI/ML ������P�¯ٱ��� (Threat Intelligence)
1.2 �V�X�������[�c���������`�N�ƶ�
1.2.1 �����Τ@���z
1.2.2 ASIC ���]��
1.2.3 ����ͨ����� (Cloud Native Firewall)
1.2.4 ����������
1.2.5 ������Y�A�� (FWaaS)
1.2.6 ��@�@�~�t��
1.3 A Brief summary of steps getting a FortiGate up and running
1.4 Setting up FortiGate for management access
1.5 Completing the FortiGate Setup wizard
1.6 Planning and configuring the MGMT, WAN, and LAN interfaces
1.6.1 Management access
1.6.2 WAN interface
1.6.3 LAN interface
1.6.4 Configuring the default route
1.6.5 Configuring the hostname
1.6.6 Ensuring internet and FortiGuard connectivity
1.7 Registering a FortiGate device
1.8 Configuring a firewall policy
1.9 Backing up the configuration
1.10 Troubleshooting your installation (Optional Knowledge)
2. Using the GUI
2.1 Connecting using a web browser
2.2 Tables
2.2.1 Filters
2.2.2 Editing objects
2.2.3 Copying rows
2.2.4 Entering Values
2.2.5 Numbers
2.3 GUI-based global search
2.3.1 Loading artifacts from a CDN
2.3.2 Accessing additional support resources
2.3.3 Command palette
2.4 Recovering missing graphical components
3. Using the CLI
3.1 Connecting to the CLI
3.1.1 Console connection
3.1.2 SSH access
3.2 CLI basics
3.2.1 Help
3.2.2 Shortcuts and key commands
3.2.3 Command tree
3.2.4 Command abbreviation
3.2.5 Adding and removing options from lists
3.2.6 Environment variables
3.2.7 Special characters
3.2.8 Using grep to filter command output
3.2.9 Language support and regular expressions
3.2.10 Screen paging
3.2.11 Changing the baud rate
3.2.12 Editing the configuration file
3.3 Command syntax
3.3.1 Notation
3.3.2 Optional values and ranges
3.3.3 next
3.3.4 end
3.4 Subcommands
3.4.1 Table subcommands
3.5 Permissions
4. Configuration and Management Tools
4.1 FortiExplorer Go and FortiExplorer
4.1.1 FortiExplorer Go
4.2 Getting started with FortiExplorer
4.3 Connecting FortiExplorer to a FortiGate with WiFi
4.4 Configure FortiGate with FortiExplorer using BLE
4.5 Running a security rating
4.6 Migrating a configuration with FortiConverter
5. Product Registration with FortiCare
5.1 FortiCare and FortiGate Cloud login
5.2 FortiCare Register button
5.3 Transfer a device to another FortiCloud account
5.4 Deregistering a FortiGate
6. FortiGate models
6.1 Differences between models
6.2 Low encryption models
6.2.1 Reasons for Using Low-Encryption Models
6.2.2 Practical Limitations of Low-Encryption Models
6.3 LEDs
6.3.1 More about Port LEDs
6.3.2 Alarm levels
6.4 Proxy-related features not supported on FortiGate 2 GB RAM models
6.5 Upgrading from previous firmware versions
7. Dashboards and Monitors
7.1 Using dashboards
7.2 Viewing device dashboards in the Security Fabric
7.3 Creating a fabric system and license dashboard
7.3.1 Example
7.4 Dashboards
7.4.1 Resetting the default dashboard template
7.4.2 Status dashboard
7.4.3 Updating system information
7.4.4 Viewing Fabric devices
7.4.5 Viewing administrators
7.4.6 Viewing logs sent for remote logging source
7.4.7 Resource widgets
7.4.8 Viewing session information for a compromised host
7.4.9 Network dashboard
7.4.10 DHCP monitor
7.4.11 IPsec monitor
7.4.12 IPsec monitor
7.4.13 SSL-VPN monitor
7.5 Assets & Identities
7.5.1 Assets
7.5.2 Assets and filtering
7.5.3 Adding MAC-based addresses to devices
7.5.4 Firewall Users monitor
7.5.5 WiFi dashboard
7.5.6 FortiAP Status monitor
7.5.7 Clients by FortiAP monitor
7.5.8 Health status
8. FortiView Monitors
8.1 Optimal and Comprehensive Template
8.2 Core FortiView monitors
8.3 Adding FortiView monitors
8.4 Using the FortiView interface
8.4.1 Real-time and historical charts
8.4.2 Data source
8.4.3 Drilldown information
8.5 Enabling FortiView from devices
8.6 FortiView sources
8.7 FortiView Sessions
8.8 FortiView Top Source and Top Destination Firewall Objects monitors
8.9 Viewing top websites and sources by category
8.10 Cloud application view
8.11 Configuring the Cloud Applications monitor
8.12 Monitoring network traffic without SSL deep inspection
9. Deploying FortiGate-VM
9.1 FortiGate-VM models and licensing
9.2 Deployment package contents
9.3 Permanent trial mode for FortiGate-VM
10. Firewall Policy
10.1 Firewall Policy Parameters
10.2 Configurations in the GUI
10.3 Configurations in the CLI
10.3.1 Firewall anti-replay option per policy
10.3.2 Deny matching with a policy with a virtual IP applied
10.3.3 Hardware acceleration
10.3.4 TCP Maximum Segment Size (MSS)
10.3.5 Adjusting session time-to-live (TTL)
10.3.6 Policy views
10.3.7 Policy match
10.4 Services
10.4.1 Predefined services
10.4.2 Custom services
10.4.3 Service groups
11. Local-in policy
11.1 Configuring the local-in policy
11.2 Virtual patching on the local-in management interface
11.3 Implicit deny rule
11.4 TTL policies
11.5 Internet service as source addresses
11.6 Logging local traffic per local-in policy
12. DoS Policy
12.1 DoS anomalies
12.2 DoS policies
13. Access control lists
14. Interface Policies
15. Source NAT
15.1 Static SNAT
15.2 Dynamic SNAT
15.2.1 IP pool types
15.2.2 One-to-one
15.2.3 Fixed port range
15.2.4 Port block allocation
15.2.5 NAT64 in FortiGate firewall
15.2.6 IP pools and VIPs as local IP addresses
15.3 Central SNAT
15.3.1 To enable central SNAT from the GUI
15.3.2 To configure central SNAT using the CLI
15.3.3 Fine-tuning source port behavior
15.4 Configuring an IPv6 SNAT policy
16. Destination NAT
16.1 Configuring VIPs
16.2 Viewing VIP overlap in security rating reports
16.3 IP pools and VIPs as local IP addresses
16.4 Virtual IP with services
17. Virtual Server Load Balancing
17.1 SSL/TLS offloading
17.2 Virtual server requirements
17.2.1 Virtual server types
17.2.2 Load balancing methods
17.2.3 Health check monitoring
17.2.4 Session persistence
17.2.5 Real servers
17.2.6 Sample of HTTP load balancing to three real web servers
17.2.7 Virtual server load balance multiplexing
18. Security Profile Inspection Modes
18.1 Flow mode inspection (default mode)
18.2 Proxy mode inspection
18.3 Inspection mode feature comparison
18.3.1 Feature comparison between Antivirus inspection modes
18.3.2 Feature comparison between Web Filter inspection modes
18.3.3 Feature comparison between Email Filter inspection modes
18.3.4 Feature comparison between DLP inspection modes
19. Antivirus
19.1 Antivirus introduction
19.1.1 Protocol comparison between antivirus inspection modes
19.1.2 Other antivirus differences between inspection modes
19.2 Antivirus techniques
19.2.1 Content disarm and reconstruction
19.2.2 Virus outbreak prevention
19.2.3 External malware block list
19.2.4 EMS threat feed
19.2.5 AI-based malware detection
19.3 Configuring an antivirus profile
19.4 Proxy mode stream-based scanning
19.5 TCP windows
19.6 Flow mode stream-based scanning
19.7 Databases
19.8 FortiSandbox database
20. Web Filter
20.1 Web filter techniques
20.2 Configuring a web filter profile
20.3 FortiGuard filter
20.4 Blocking a web category
20.5 Allowing users to override blocked categories
20.6 Issuing a warning on a web category
20.7 Authenticating a web category
20.8 Customizing the replacement message page
20.9 Category usage quota
20.10 Restrict YouTube and Vimeo access
20.11 Block invalid URLs
20.12 URL filter
20.13 Block malicious URLs discovered by FortiSandbox
20.14 Web content filter
20.15 Credential phishing prevention
21. Video Filter
21.1 Configuring a video filter profile
21.2 YouTube API key
21.3 Filtering based on FortiGuard categories
21.4 Verifying that the video is blocked
21.5 Troubleshooting and debugging
21.6 Filtering based on YouTube channel
21.6.1 Identifying the YouTube channel ID
21.7 Filtering based on title
21.8 Filtering based on description
22. DNS filter
22.1 DNS filter behavior in proxy mode
22.2 Configuring a DNS filter profile
22.3 FortiGuard category-based DNS domain filtering
22.4 Botnet C&C domain blocking
22.5 Botnet C&C IPDB blocking
22.6 DNS safe search
22.7 DNS over QUIC and DNS over HTTP3 for transparent and local-in DNS modes
23. Inline CASB
23.1 Privilege control
23.2 Safe search
23.3 Tenant control
23.4 UTM bypass
23.5 Microsoft CoPilot Commercial Data Protection
24. Intrusion prevention
24.1 Signature-based defense
24.1.1 IPS signatures
24.1.2 Protocol decoders
24.1.3 IPS engine
24.1.4 IPS sensors
24.1.5 IPS filters
24.1.6 Custom and predefined signature entries
24.1.7 Overriding the default action
24.1.8 Policies
24.2 IPS configuration options
24.2.1 Malicious URL database for drive-by exploits detection
24.2.2 IPS signature rate count threshold
24.2.3 Botnet C&C
24.2.4 Extended IPS database
24.2.5 IPS engine-count
24.2.6 OT threat definitions
24.2.7 Fail-open
24.2.8 IPS buffer size
24.2.9 Session count accuracy
24.2.10 Protocol decoders
24.3 SCTP filtering capabilities
24.4 IPS signature filter options
24.4.1 Hold time
24.4.2 Viewing on hold information in the GUI
24.4.3 CVE pattern
24.4.4 IPS sensor attributes
24.5 IPS with botnet C&C IP blocking
24.6 IPS sensor for IEC 61850 MMS protocol
24.6.1 MMS (Manufacturing Message Specification) usage scenario
24.6.2 How FortiGate helps in securing MMS/ICCP communications
24.6.3 IPS signatures for the operational technology security service
25. VPN
25.1 Site-to-site VPN
25.1.1 Create a Phase 1 Interface
25.1.2 Phase 2 configuration
25.1.3 Adding routes for Route-Based VPN
25.1.4 Configuring Security Policy to allow traffic to pass through VPN tunnel
25.2 VPN IPsec troubleshooting
25.2.1 Understanding VPN related logs
25.3 IPsec related diagnose commands
25.4 VPN and ASIC offload
26. Remote Access VPN
26.1 FortiClient as dialup client
26.2 L2TP over IPsec
26.3 FortiGate as dialup client
27. Virtual Domains
27.1 VDOM overview
27.1.1 Multi-VDOM mode
27.1.2 Global settings
27.1.3 Global and per-VDOM resources
27.1.4 Management VDOM
27.1.5 VDOM types
27.1.6 Administrator roles and views
27.1.7 Inter-VDOM routing
27.1.8 Best practices
27.2 Enable multi-VDOM mode
27.2.1 To enable VDOMs in the GUI:
27.3 Management VDOM
27.4 Global and per-VDOM resources
27.5 Creating Traffic Type VDOM
27.6 Create per-VDOM administrators
27.7 Backing up and restoring configurations in multi-VDOM mode
 �I�ڡC
�I�ڡC