(在家觀看 = 0%,在校觀看 = 100%)
100% 在校觀看日期及時間:
自由選擇,點選以下地區觀看辦公時間及位置
課時: 24 小時
享用時期: 8 星期。進度由您控制,可快可慢。
課堂錄影導師:Larry
在校免費試睇:首 3 小時,請致電以上地點與本中心職員預約。
本課程提供在校免費重睇及導師解答服務。
(在家觀看 = 100%,在校觀看 = 0%)
100% 在家觀看日期及時間:
每天 24 小時全天候不限次數地觀看
課時: 24 小時
享用時期: 8 星期。進度由您控制,可快可慢。
課堂錄影導師:Larry
在校免費試睇:首 3 小時,請致電以上地點與本中心職員預約。
本課程提供導師解答服務。
| 本實戰課程只會由導師於堂上進行實習,以確保導師能於有限的教學時間流暢地教授眾多的理論及實習。 |
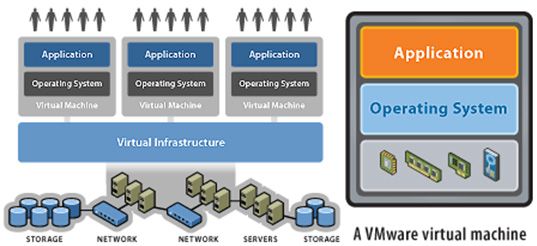
透過虛擬化技術,改善 IT 資源和應用程式的效率與可用性。從去除老舊的「一部伺服器,一個應用程式」模式開始,然後在每部實體機器上執行多部虛擬機。讓您的 IT 管理員不必再耗費大量時間管理伺服器,而有餘裕發明創新。在非虛擬化資料中心大約有 70% 的典型 IT 預算耗費在維護現有的基礎架構上,只剩少數預算可用來創新。
在備受肯定的 VMware 虛擬平台上建置的自動化資料中心則讓您能夠比以往更快速、更有效率地回應市場趨勢。VMware vSphere會依需要提供資源、應用程式,甚至是伺服器。使用 VMware vSphere 進行資源整合與提供高度可用(High Availability)的機器後,VMware 客戶一般可省下 50-70% 的整體 IT 成本。
- 可同時在單一電腦上執行多個作業系統,如 Windows、Linux 等。
- 可在 Mac 上執行 Windows,建立虛擬 PC 環境,以便使用各種 Windows 應用程式。
- 提升能源效率、降低對硬體的需求並提高伺服器與管理人員間的比例,以降低資金成本
- 確保企業應用程式能展現最高的可用性與效能
- 藉由改善災難復原解決方案並提供高可用性的資料中心,維持業務續航力。
- 加快桌面平台部署的速度,減少起因於應用程式衝突的客服支援,進而改善企業桌面平台的管理與控制
| 課程名稱: |
VMware vSphere 6.5 實戰進階課程 (適合有 6.5 基礎知識人士報讀) - 簡稱:VMware vSphere Training Course (6.5 Advanced) |
| 課程時數: | 合共 24 小時 |
| 適合人士: | 對電腦網絡安裝及使用有基本認識 |
| 授課語言: | 以廣東話為主,輔以英語 |
| 課程筆記: | 本中心導師親自編寫英文筆記 |
|
課程名稱:VMware vSphere 6.5 實戰進階課程 (適合有 6.5 基礎知識人士報讀) - 簡稱:VMware vSphere Training Course (6.5 Advanced) |
詳細教授內容 :
1. Advanced Networking
1.1 Setup vMotion Network
1.2 Setup FT Network
1.3 Setup iSCSI Network
1.4 Bind iSCSI Adapter to vSwitch
1.5 Changing the Path Select Policy by using PowerCLI
1.6 More about Path Select Policy
1.6.1 Fixed (VMware)
1.6.2 Most Recently Used (VMware)
1.7 vSphere Distributed Switch
1.7.1 Distributed Switch Architecture
1.7.2 Uplink port group
1.7.3 Distributed port group
1.7.4 Distributed Switch Data Flow
1.7.5 Creating a Distributed Switch for Virtual Machine traffic
1.7.6 Network I/O Control
1.7.7 Bandwidth Allocation for System Traffic
1.7.8 Traffic Shaping Policy in a Distributed Switch environment
1.7.9 Port Mirroring
1.7.10 Traffic Filtering and Marking Policy
1.7.11 Switch Discovery Protocol
1.7.12 Backing up a Virtual Distributed Switch
2. High Availability and Fault Tolerance
2.1 How vSphere HA Works
2.1.1 Host Failure Types and Detection
2.1.2 Master and Slave Hosts
2.1.3 Datastore Heartbeating
2.1.4 Using vSphere HA and DRS Together
2.1.5 vSphere HA Admission Control
2.1.6 Host Failures Cluster Tolerates Admission Control Policy
2.1.7 Slot Size Calculation
2.1.8 Using Slots to Compute the Current Failover Capacity
2.1.9 Advanced Runtime Info
2.1.10 Admission Control Using Host Failures Cluster Tolerates Policy
2.1.11 Percentage of Cluster Resources Reserved Admission Control Policy
2.1.12 Computing the Current Failover Capacity
2.1.13 Admission Control Using Percentage of Cluster Resources Reserved Policy
2.1.14 Specify Failover Hosts Admission Control Policy
2.1.15 Choosing an Admission Control Policy
2.2 Creating vSphere HA Cluster
2.2.1 Setup the Lab
2.2.2 Create Cluster
2.2.3 Cluster Features
2.3 Fault Tolerance for Virtual Machine
2.3.1 How Fault Tolerance Works
2.3.2 Fault Tolerance Interoperability
2.4 Turn On Fault Tolerance
2.4.1 Case 1
2.4.2 Case 2
2.4.3 More about vSphere Fault Tolerance in an HA-Enabled Cluster
3. Datastore Cluster
3.1 Initial Placement and Ongoing Balancing
3.2 Storage Migration Recommendations
3.3 Create Datastore Cluster
3.4 Use Of Datastore Cluster
4. Storage With SSD
4.1 Solid State Disks Enablement
4.2 Benefits of SSD Enablement
4.2.1 Auto-Detection of SSD Devices
4.2.2 Best Practices for SSD Devices
4.2.3 Host Cache Configuration
4.3 Flash Read Cache for Virtual Machine
5. Virtual SAN
5.1 Requirements
5.1.1 vSphere Requirements
5.1.2 Storage Requirements
5.1.3 Network Requirements
5.2 Setup vSAN
5.2.1 Prepare and Turn On vSAN
5.2.2 Configure VM Port Group for vSAN
5.2.3 Configure vSAN
5.3 Using vSAN Datastore
5.4 Using VM Storage Policy
5.4.1 Create Storage Policy
5.4.2 Using Storage Policy
5.4.3 Create Raid 1 Policy
5.4.4 Change Virtual Machine Storage Policy
5.5 Simulate Host Fail
5.6 vSAN iSCSI target
5.7 More about vSAN Stretch Clusters
5.7.1 About vSAN Stretch Clusters
5.7.2 vSAN Stretch Clusters deployment
5.7.3 Using Fault Domains in Stretch Clusters
5.7.4 Stretched cluster with RAID-5 erasure coding local failure protection
5.7.5 Site Affinity in Stretch Clusters
5.7.6 Improved Device Handling in degraded situation
5.7.7 Rebuilding and Resynchronization Throttling in vSAN Stretch Cluster
5.8 Common Troubleshooting and Debug commands
6. Auto Deploy
6.1 Understanding vSphere Auto Deploy
6.1.1 Introduction to Auto Deploy
6.1.2 Rules and Rule Sets
6.2 Setup Storage with NFS
6.2.1 Install Omni OS
6.2.2 Install Napp-it
6.3 Install TFTP Server
6.4 Enable vSphere Auto Deploy
6.5 Configure DHCP Server for PXE Boot
6.6 Setup Auto Deploy
6.6.1 Setup Boot Image
6.6.2 Setup Host Profile
6.6.3 Create Production Image
6.6.4 Create New Deploy Rule
7. Security Certificates
7.1 Prepare Certificate
7.1.1 Prepare Certificate Template
7.2 Replace Certificates
8. Advanced vCenter Installation
8.1 vCenter Server Appliances
8.2 Deploy VCSA
8.3 Replacing VMCA and TLS certificate on VCSA
8.4 Use of vCenter Server Appliances
8.5 Install PSC on ESXA3
8.6 Install Standalone VCSA with External PSC
8.7 Reconfigure VCSA with Embedded PSC to use vCenter Server with External PSC
9. vCenter HA
9.1 What is vCenter HA
9.1.1 Plan the vCenter HA Deployment
9.1.2 Configure the Network
9.1.3 Configure vCenter HA with the Basic Option
9.1.4 Configure vCenter HA with the Advanced Option
9.2 Setup vCenter HA
9.3 Test Failover
9.4 Simulate Host Fail
9.5 Remove vCenter HA
 付款。
付款。