(在家觀看 = 0%,在校觀看 = 100%)
100% 在校觀看日期及時間:
自由選擇,點選以下地區觀看辦公時間及位置
課時: 24 小時
享用時期: 12 星期。進度由您控制,可快可慢。
課堂錄影導師:Larry
在校免費試睇:首 3 小時,請致電以上地點與本中心職員預約。
本課程提供在校免費重睇及導師解答服務。
(在家觀看 = 100%,在校觀看 = 0%)
100% 在家觀看日期及時間:
每天 24 小時全天候不限次數地觀看
課時: 24 小時
享用時期: 12 星期。進度由您控制,可快可慢。
課堂錄影導師:Larry
在校免費試睇:首 3 小時,請致電以上地點與本中心職員預約。
本課程提供導師解答服務。
Preface
The role of a Microsoft security operations analyst is essential in ensuring that the organization's information technology systems are secure from any possible threat. This is achieved through collaboration with various stakeholders in the organization to assess the risk levels and determine the necessary measures to mitigate them.
One of the primary responsibilities of the security operations analyst is to monitor and respond to any potential threats within the environment.
This is done through the use of various security solutions, including Microsoft Sentinel, Microsoft Defender for Cloud, Microsoft 365 Defender, and third-party security products.
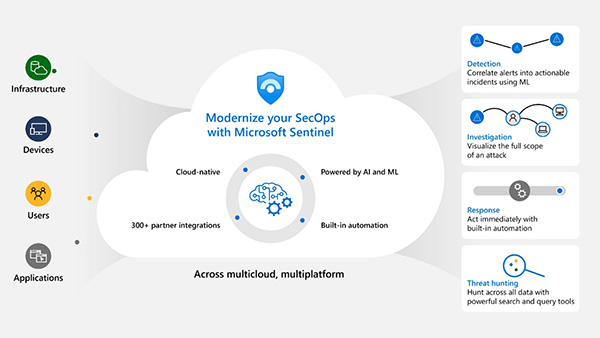
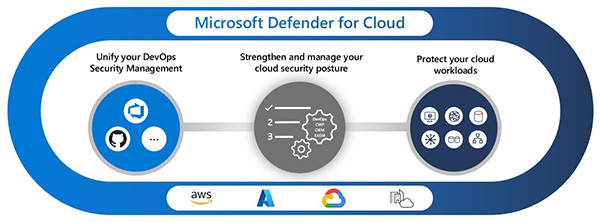
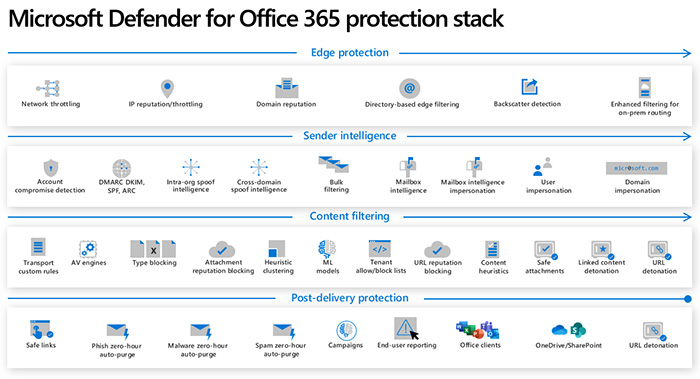
The security operations analyst should be highly experienced, practiced, skilled and very knowledgeable in these above tools' operation to effectively utilize them to secure the organization's systems.
In addition to responding to threats, the security operations analyst should also identify areas for improvement in threat protection practices.
This includes analyzing data from security solutions and using it to advise on changes to security practices, policies, and procedures. If any violations of organizational policies are detected, the security operations analyst should refer them to the appropriate stakeholders for further action.
To be successful in this role, candidates should have knowledge of various attack vectors and cyber threats, as well as incident management.
They should also be proficient in using Kusto Query Language (KQL), which is a query language used to analyze data in Azure Log Analytics and Azure Application Insights.
Moreover, candidates should have a good understanding of Microsoft 365 and Azure services to be able to consume the operational output of the security tools.
Overall, the role of a Microsoft security operations analyst is critical in ensuring the organization's information technology systems are secure from potential threats. Their ability to rapidly respond to active attacks and identify areas for improvement in threat protection practices is key to reducing organizational risk.

Microsoft Certified Security Operations Analyst Associate
The Certification “Microsoft Certified Security Operations Analyst Associate” validates your capability to implement security controls and threat protection, manage identity and access, and protect data, applications, and networks in Azure cloud, Microsoft 365 and multi-cloud environments as part of your global infrastructure.
About the course
Our training course will guide you through carefully selected exam topics, along with real-life examples, practical demonstration and business cases of implementing, verifying and maintaining various Microsoft Sentinel, Defender for Cloud and Defender for M365 Security features.
Evaluations, Pros and Cons and may be comparisons of various Microsoft Security products would be verbally provided throughout the training course.
As Microsoft has been partnering with multiple 3rd party vendors and built security-related ecosystems, it is inevitable that a small portion of the course time would be spent on briefly discussing popular partner security solutions.
Our senior instructor Mr. Larry Chan would give you advise, tricks and tips on various cloud security-related products.
| 課程名稱: |
Microsoft Certified Security Operations Analyst Associate (1 科商務雲端保安) 國際認可證書課程 - 簡稱:Microsoft Security Operations Training Course |
| 課程時數: | 24 小時 (共 8 堂,共 1 科) |
| 適合人士: | 有志考取Microsoft Certified Security Operations Analyst Associate證書人士; 或 有少量 Microsoft 365 / Office 365使用經驗人士; 或 對多重雲端保安技術有興趣人士 |
| 授課語言: | 以廣東話為主,輔以英語 |
| 課程筆記: | 本中心導師親自編寫英文為主筆記,而部份英文字附有中文對照。 |
| 1. 模擬考試題目: | 本中心為學員提供模擬考試題目,每條考試題目均附有標準答案。 |
| 2. 時數適中: | 本中心的 Microsoft Certified Security Operations Analyst Associate (1 科商務雲端保安) 國際認可證書課程時數適中,有 24 小時。
令學員能真正了解及掌握課程內容,而又能於 3 個月內考獲以下 1 張國際認可證書:
|
| 3. 導師親自編寫筆記: | 由本中心已擁有五項 MCITP,十多項 MCTS、MCSA 及 MCSE 資格,並有教授 Microsoft 相關課程 20 年以上經驗的資深導師 Larry Chan 親自編寫筆記,絕對適合考試及實際管理之用,令你無須「死鋤」如字典般厚及不適合香港讀書格調的書本。 |
| 4. 一人一機上課: |
本課程以一人一機模式上課。 |
| 5. 免費重讀: | 傳統課堂學員可於課程結束後三個月內免費重看課堂錄影。 |
Microsoft 已公佈考生只要通過以下 1 個 Security Operations 相關科目的考試,便可獲發 Microsoft Certified Security Operations Analyst Associate 國際認可證書:
| 考試編號 | 科目名稱 |
| SC-200 | Microsoft Security Operations Analyst |
本中心為Microsoft指定的考試試場。報考時請致電本中心,登記欲報考之科目考試編號、考試日期及時間
(最快可即日報考)。臨考試前要出示身份證及繳付每科HK$943之考試費。 考試不合格便可重新報考,不限次數。欲知道作答時間、題目總數、合格分數等詳細考試資料,可瀏覽本中心網頁 "各科考試分數資料"。 |
|
課程名稱:Microsoft Certified Security Operations Analyst Associate (1 科商務雲端保安) 國際認可證書課程 - 簡稱:Microsoft Security Operations Training Course |
SC-200 Microsoft Security Operations Analyst (24 hrs)
1. Introduction to Microsoft 365 threat protection
1.1 About M365 Defender product family
1.2 Extended Detection & Response (XDR) response use cases
1.2.1 Detection of Threat
1.2.2 Remediation
1.2.3 Share Intelligence and Restore Access
1.2.4 Access Restricted
1.2.5 Access Restored
1.3 Microsoft 365 Defender in a Security Operations Center (SOC)
1.3.1 Security Operations Model - Functions and Tools
1.3.2 Triage and Automation
1.3.3 Investigation and Incident Management (Tier 2)
1.3.4 Hunt and Incident Management (Tier 3)
1.3.5 Threat intelligence
1.4 Microsoft Security Graph
1.4.1 About Microsoft Graph
1.4.2 Microsoft Graph Security API
1.4.3 Use the Microsoft Graph Security API
2. Mitigate incidents using Microsoft 365 Defender
2.1 Defender Portal
2.2 Required roles and permissions
2.3 Manage incidents
2.4 Investigate incidents
2.4.1 Incident overview
2.4.2 Alerts
2.4.3 Devices
2.4.4 Users
2.4.5 Mailboxes
2.4.6 Apps
2.4.7 Investigations
2.4.8 Evidence and Responses
2.4.9 Graph
2.5 Manage and investigate alerts
2.5.1 Manage investigate alerts
2.5.2 Alert management
2.5.3 Severity
2.5.4 Suppress alerts
2.5.5 Change the status of an alert
2.5.6 Alert classification
2.5.7 Add comments and view the history of an alert
2.5.8 Investigate using the alert story
2.5.9 Take action from the details pane
2.6 Automated Investigation
2.6.1 How the automated investigation starts
2.6.2 How an automated investigation expands its scope
2.6.3 How threats are remediated
2.6.4 Automation levels in automated investigation and remediation capabilities
2.6.5 Review or change the automation level for device groups
2.6.6 Levels of automation
2.7 Action Center
2.7.1 Viewing action source details
2.8 Reporting suspicious content to Microsoft
2.9 Advanced Hunting
2.9.1 Data freshness and update frequency
2.9.2 Data schema
2.9.3 What you can find in these schema tables?
2.9.4 Example usage scenario for Advanced Hunting
2.10 Investingating Azure AD sign-in logs
2.11 Secure Score
2.11.1 Introduction to Secure score
2.11.2 How secure score works
2.11.3 Secure score dashboard
2.12 Analyze threat analytics
2.12.1 Background information of Threat Analytics
2.12.2 Assess impact on your organization
2.12.3 Review security resilience and posture
2.12.4 View reports per threat tags
2.12.5 Set up email notifications for report updates
3. Identity and Access Management in M365 Subscription
3.1 Creating and Managing Microsoft 365 for Business Subscription
3.2 Configuring Custom Domain Name for Microsoft 365
3.3 Creating Users and Assign licenses
3.4 Evolution of identity technology
3.4.1 Identity challenges
3.4.2 Identity is the new control plane
3.4.3 Identity governance process
3.5 Zero Trust Model (零信任安全模型)
3.5.1 Zero Trust concepts
3.5.2 Zero Trust principles
3.5.3 Zero Trust components
3.6 Plan for a Zero Trust model
3.6.1 First step to enable a Zero Trust model—strong identity and access management
3.6.2 Zero Trust using Azure AD conditional access
3.6.3 Zero Trust networking
3.7 Plan your identity and authentication solution
3.7.1 Microsoft 365 identity models
3.7.2 Principal of Password Hash Synchronization
3.7.3 Monitoring AD Connect Synchronization Health
3.7.4 Azure AD Connect Sync Insight
3.7.5 Sync Latency
3.7.6 Sync Object Changes
3.7.7 Directory synchronization
3.7.8 Azure AD Connect cloud provisioning
3.8 Accounts and Roles
3.8.1 User identities
3.8.2 Creating users with Windows PowerShell
3.8.3 Manage user accounts and licenses
3.8.4 About Groups
3.9 Password Managment
3.9.1 Password Expiration
3.10 Introduction to Multi-factor authentication
3.10.1 Require MFA
3.10.2 Self-service password reset
3.10.3 Self-service password reset example
3.11 Password alternatives
3.11.1 Passwordless authentication with Azure AD
3.11.2 Microsoft Authenticator
3.11.3 Windows Hello for Business
3.12 Azure AD Smart Lockout
3.12.1 Verify On-premises Account Lockout Policy
3.12.2 Manage Azure AD Smart Lockout Values
4. Manage users with directory synchronization
4.1 Recovering a user account that was accidentally deleted
4.1.1 More about deleted Active Directory Objects
4.1.2 About Restoring on-premises Active Directory objects by Recycle Bin
4.1.3 Enabling the Active Directory Recycle Bin
4.1.4 Restoring Active Directory Objects
4.2 Recovering from unsynchronized deletes
4.3 Enhanced user management
4.3.1 Password writeback
4.3.2 Device writeback
4.4 Manage groups with directory synchronization
4.5 Azure AD Connect Sync Security Groups
4.6 Troubleshoot directory synchronization
4.6.1 Deactivate and Reactivate Directory Synchronization
4.6.2 View directory synchronization errors in the Microsoft 365 admin center
4.7 Unhealthy Identity Synchronization Notification
4.7.1 Synchronization Service Manager
4.7.2 Troubleshoot password hash synchronization with Azure AD Connect
4.8 Azure AD Identity Protection
4.8.1 Risk detection and remediation
4.8.2 Risk investigation
4.8.3 Detect vulnerabilities and risk events
4.8.4 Azure Active Directory risk events
4.8.5 Users with Leaked credentials
4.9 Azure Active Directory Identity Protection workflow
4.9.1 Self-remediation workflow
4.9.2 Administrator remediation workflow
4.10 Plan your investigation
4.10.1 Mitigation sign-in risk events
4.10.2 Mitigation Best Practices
4.10.3 User risk
4.10.4 Closing risk events manually
4.10.5 Remediating user risk events
4.10.6 Azure Identity Protection notifications
4.11 Detect risks with Azure AD (Entra ID) Identity Protection policies
4.11.1 Sign-in Risk Policy
4.11.2 User Risk Policy
4.11.3 Multifactor authentication (MFA) registration policy
4.12 Investigate and remediate risks detected by Azure AD Identity Protection
4.12.1 Reports for Investigating risks
4.12.2 Investigation Framework
4.12.3 Remediate risks and unblock users
4.13 Simulating Risk Detections
4.13.1 Anonymous IP address
4.13.2 Unfamiliar sign-in properties
4.13.3 Atypical travel
4.13.4 Leaked Credentials for Workload Identities
5. Identity and Access Management
5.1 Introduction to Application Management
5.2 Improve productivity with SSO
5.2.1 Seamless Single Sign-On (SSO)
5.2.2 Key features of Seamless SSO
5.3 Azure AD (or Entra ID) App gallery
5.4 Azure AD (or Entra ID) application proxy
5.5 Secure hybrid access
5.6 Azure AD (or Entra ID) Identity Governance
5.6.1 Access lifecycle
5.6.2 Privileged access lifecycle
5.7 Conditional Access
5.7.1 Conditional access policies
5.7.2 Implementing cloud-based Azure Multi-Factor Authentication
5.7.3 Azure AD (or Entra ID) security defaults
5.7.4 Installing Microsoft Authenticator App
5.7.5 Testing Azure MFA
5.7.6 Configure Azure MFA Settings
5.7.7 Block and unblock users
5.7.8 Fraud Alert
5.7.9 Azure AD (or Entra ID) Sign-ins report
5.7.10 More about Security Defaults
5.7.11 Conditional access report-only mode
5.8 Managing Device Access
5.8.1 Plan for device compliance
5.8.2 Configure conditional users and groups
5.8.3 Create conditional access policies
5.8.4 Applying a conditional access policy
5.8.5 Conditional access with Intune
5.8.6 Monitor enrolled devices
5.9 Role Based Access Control (RBAC)
5.9.1 Plan for RBAC
5.9.2 Azure RBAC roles, and Azure AD (or Entra ID) administrator roles
5.9.3 Custom RBAC Roles
5.9.4 Azure AD (or Entra ID) B2B External Access solution
5.9.5 Office 365 external sharing and Azure AD (or Entra ID) B2B collaboration
5.9.6 Microsoft Teams external and guest access
5.10 Azure AD (or Entra ID) Priviliged Identiy Management
Key PIM Terminology and High-Level view of PIM flow
5.10.1 Enabling Azure AD (or Entra ID) Privileged Identity Management
5.10.2 Assigning Azure Resource Roles in PIM
5.10.3 Activating an Eligible resource role in Azure AD (or Entra ID) PIM
5.10.4 JIT Admin Access
5.10.5 Audit PIM
6. Configuring a Microsoft Sentinel Environment
6.1 Introduction to SIEM (Security Information and Event Management)
6.2 Principals of Microsoft Sentinel
6.2.1 Data connectors
6.2.2 Log retention
6.2.3 Workbooks
6.2.4 Analytics alerts
6.2.5 Threat hunting
6.2.6 Incidents and investigations
6.2.7 Automation playbooks
6.3 Usage Scenario of Microsoft Sentinel
6.4 Planning for the Microsoft Sentinel workspace
6.4.1 Single-tenant single workspace
6.4.2 Single-tenant with regional Microsoft Sentinel workspaces
6.4.3 Multi-tenant workspaces
6.4.4 Use the same log analytics workspace as Microsoft Defender for Cloud
6.5 Querying Logs in Micorsoft Sentinel
6.5.1 Understand Microsoft Sentinel tables
6.6 Watchlist
6.7 Threat Intelligence in Microsoft Sentinel
6.7.1 The Principals behind
7. Microsoft Defender for Identity
7.1 Why use Microsoft Defender for Identity?
7.2 Monitor and profile user behavior and activities
7.2.1 Protect user identities and reduce the attack surface
7.2.2 Identify suspicious activities and advanced attacks across the cyber-attack kill-chain
7.3 Improve your security posture
7.3.1 Configure Microsoft Defender for Identity
7.3.2 Generate Microsoft Defender for Identity reports
 付款。
付款。