(在家觀看 = 0%,在校觀看 = 100%)
100% 在校觀看日期及時間:
自由選擇,點選以下地區觀看辦公時間及位置
課時: 36 小時
享用時期: 18 星期。進度由您控制,可快可慢。
課堂錄影導師:Larry
在校免費試睇:首 3 小時,請致電以上地點與本中心職員預約。
本課程提供在校免費重睇及導師解答服務。
(在家觀看 = 100%,在校觀看 = 0%)
100% 在家觀看日期及時間:
每天 24 小時全天候不限次數地觀看
課時: 36 小時
享用時期: 18 星期。進度由您控制,可快可慢。
課堂錄影導師:Larry
在校免費試睇:首 3 小時,請致電以上地點與本中心職員預約。
本課程提供導師解答服務。
如果您是部署及管理 Microsoft 365,並是以雲端和混合式環境來執行 Microsoft 365 租用戶層級 (Tenant-level) 的系統管理員,那麼此專家級 MCAE 認證便是專為您而設計。
身為 Microsoft 365 的系統管理員,您會:
- 為所有 Microsoft 365 工作負載 (workloads) 進行整合 (Integration)。
- 協調多個 Microsoft 365 工作負載。
- 與負責工作負載、基礎結構 (infrastructure)、身份識別 (identity)、安全性 (security)、合規性 (compliance)、端點 (endpoints) 和應用程式 (enterprise applications) 的架構師和其他系統管理員合作。
要成功考取到此專家級 MCAE 認證,您必須具備所有 Microsoft 365 工作負載、Microsoft Entra ID (or Azure AD)、Exchange Online、Teams Collaboration、Purview 及 Defender XDR 的實際經驗,並至少管理過其中一項。而您也應該具備下列的工作知識:
- TCP/IP Networking
- Windows Server administration
- DNS administration
- PowerShell usage
本課程將會幫助您強化上述各項知識及技能,令您成功通過考試並獲取 MCAE 認證。

Microsoft 365 Certified Administrator Expert
"Microsoft 365 Certified Administrator Expert" 是一項專家級認證,它是相應的 Associate 級別認證的下一步,亦是微軟最高級別的認證。
這項專家級認證核實了您在 Microsoft 365 和混合環境中的下列進階能力:
- 設計和實施安全控制和威脅防護
- 管理身份和訪問權限
- 保護數據
- 應用程式和網絡
本課程將示範現實商業需求的操作例子,並實現在最新操作系統中執行、驗證和維護各種 Microsoft 365 和混合環境的安全功能,從而強化您應付專家級考試時所須的熱門知識。
在整個培訓課程中,我們將提及對不同 Microsoft 安全產品的評估、優缺點及可能的比較。由於 Microsoft 已經與多個第三方供應商建立合作關係及網絡安全生態系統,因此,課程中會用一小部份時間來簡要討論熱門合作夥伴的安全解決方案,並將其整合到 Microsoft 365 的商務雲端環境中。
由於對風險的可見性 (extended detection) 及應對 (response) 第三方風險的能力變得越來越重要及具影響力,甚至會影響了互聯的業務世界,因此在整個課程中,將討論多種治理和風險合規 (GRC) 標準和技術策略,這使您和您的組織能夠可靠地實現安全目標,應對不確定性並以誠信行事。
我們的資深導師 Mr. Larry Chan 將就各種雲安全相關產品提供建議、技巧和貼士。| 課程名稱: |
Microsoft 365 Certified Administrator Expert (1科商務雲端專家) 國際認可證書課程 - 簡稱:Administrator Expert Training Course |
| 課程時數: | 36 小時 (共 12 堂,共 1 科) |
| 適合人士: | 有志考取 Microsoft 365 Certified Administrator Expert 證書人士 |
| 授課語言: | 以廣東話為主,輔以英語 |
| 課程筆記: | 本中心導師親自編寫英文為主筆記,而部份英文字附有中文對照。 |
| 1. 模擬考試題目: | 本中心為學員提供模擬考試題目,每條考試題目均附有標準答案。 |
| 2. 時數適中: | 本中心的 Microsoft 365 Certified Administrator Expert (1科商務雲端專家) 國際認可證書課程時數適中,有36小時。 令學員能真正了解及掌握課程內容,而又能於短時間內考獲以下 1 張國際認可證書:
|
| 3. 導師親自編寫筆記: | 由本中心已擁有五項 MCITP , 十多項 MCTS,MCSA 及 MCSE 資格,並有教授 Microsoft 相關課程 20年以上經驗的資深導師 Larry Chan 親自編寫筆記,絕對適合考試及實際管理之用,令你無須「死鋤」如字典般厚及不適合香港讀書格調的書本。 |
| 4. 一人一機上課: | 本課程以一人一機模式上課。 |
| 5. 免費重讀: | 傳統課堂學員可於課程結束後三個月內免費重看課堂錄影。 |
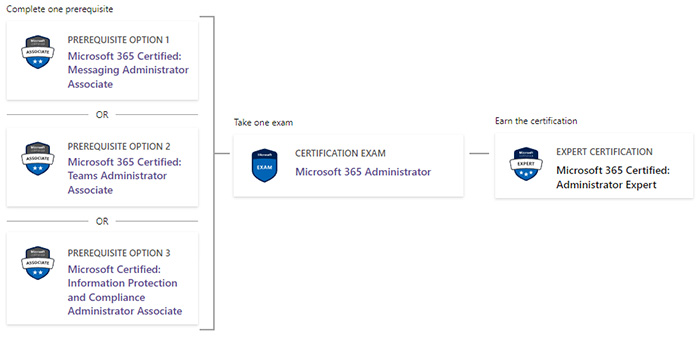
Microsoft 已公佈:
- Microsoft 365 Certified Messaging Administrator Associate 認證持有人 (即已通過入門級 MS-203 考試的人士) 或
- Microsoft 365 Certified Teams Administrator Associate 認證持有人 (即已通過入門級 MS-700 考試的人士) 或
- Microsoft Certified Information Protection and Compliance Administrator Associate 認證持有人 (即已通過入門級 SC-400 考試的人士)
| 考試編號 | 科目名稱 |
| MS-102 | Microsoft 365 Administrator |
本中心為Microsoft指定的考試試場。報考時請致電本中心,登記欲報考之科目考試編號、考試日期及時間
(最快可即日報考)。臨考試前要出示身份證及繳付每科HK$943之考試費。 考試不合格便可重新報考,不限次數。欲知道作答時間、題目總數、合格分數等詳細考試資料,可瀏覽本中心網頁 "各科考試分數資料"。 |
|
課程名稱:Microsoft 365 Certified Administrator Expert (1科商務雲端專家) 國際認可證書課程 - 簡稱:Administrator Expert Training Course |
MS-102 Microsoft 365 Administrator (36 hrs)
1. Configure Microsoft 365 Experience
1.1 Explore your Microsoft 365 cloud environment
1.1.1 Microsoft 365 subscriptions and plans
1.1.2 Build your cloud-computing foundation on a Microsoft 365 subscription and a Microsoft Entra tenant
1.1.3 Microsoft 365 plans that don't create a Microsoft Entra tenant
1.1.4 Licenses
1.1.5 Organizations with multiple Microsoft Entra tenants
1.1.6 Tenant information
1.1.7 Attributes of a well-designed Microsoft Entra tenant
1.2 Configure your Microsoft 365 organizational profile
1.2.1 Update your organization's theme
1.3 Manage your tenant subscriptions in Microsoft 365
1.4 Integrate Microsoft 365 with customer engagement apps
1.4.1 Purchase services page in the Microsoft 365 admin center
1.4.2 Assign services
1.4.3 Marketplace in the Microsoft Azure portal
1.5 Configure tenant-level sharing settings for SharePoint and OneDrive
1.6 Configure tenant-level settings for Microsoft Teams
1.6.1 Teams meeting settings
1.7 Enable Unified Audit Logging in Microsoft 365
1.8 Complete your tenant configuration in Microsoft 365
2. Manage users, licenses, guests, and contacts
2.1 Determine the user identity model for your organization
2.1.1 Cloud identities
2.1.2 Synchronized identities
2.1.3 Federated identities
2.1.4 Determining the best model for your organization
2.2 Create user accounts in Microsoft 365
2.2.1 Creating users with the Microsoft 365 admin center
2.2.2 Creating users with the “Add multiple users” option
2.2.3 Creating users with Windows PowerShell
2.3 Manage user account settings in Microsoft 365
2.3.1 Manage user accounts in the Microsoft 365 admin center
2.4 Manage user licenses in Microsoft 365
2.4.1 Assigning a license
2.4.2 Using Microsoft Graph PowerShell to manage user licenses
2.5 Recover deleted user accounts in Microsoft 365
2.5.1 Deleting a user account
2.5.2 Restoring a deleted user account
2.6 Create and manage guest users
2.6.1 Understanding guest accounts in Microsoft 365
2.6.2 External collaboration settings
2.6.3 Restrict guest access permissions in Microsoft Entra ID
2.6.4 Invitation redemption
2.6.5 Add guests in Microsoft Entra ID
2.6.6 Invitation redemption flow
2.6.7 Redemption process and sign-in through a common endpoint
2.6.8 Redemption process through a direct link
2.7 Collaborate with guests in a SharePoint site
2.7.1 Configure the Microsoft Entra ID external collaboration settings
2.7.2 Configure the SharePoint organization-level sharing settings
2.7.3 Create a site
2.7.4 Configure the SharePoint site-level sharing settings
2.7.5 Invite users
2.8 Create and manage contacts
2.8.1 Permissions needed to create mail contacts
2.8.2 Create a contact using the Microsoft 365 admin center
2.8.3 Use Exchange Online PowerShell to modify mail contacts
2.8.4 Use Exchange Online PowerShell to remove mail contacts
3. Manage groups in Microsoft 365
3.1 Group Types in Microsoft 365
3.1.1 Collaboration spaces for Microsoft 365 groups
3.1.2 How Microsoft 365 Groups work with Teams
3.1.3 Group membership
3.1.4 Deleting groups and teams
3.2 Create and manage groups in Microsoft 365
3.2.1 Nesting groups
3.2.2 Deleting and restoring groups
3.2.3 Manage group-based licensing in Microsoft Entra ID
3.3 Create dynamic groups using Microsoft Entra rule builder
3.3.1 Rule syntax for a single expression
3.3.2 Supported expression operators
3.3.3 Rules with complex expressions
3.3.4 A Rule to include all users
3.3.5 A Rule to include all devices
3.3.6 Custom Extension Properties
3.4 Microsoft 365 group naming policy
3.4.1 Prefix-suffix naming policy
3.4.2 Custom blocked words
3.4.3 Configure Microsoft 365 groups naming policy using Microsoft Entra admin center
3.4.4 User experiences with naming policy
3.4.5 Outlook web client experience
3.4.6 Outlook Desktop experience
3.4.7 License requirements
3.4.8 Microsoft 365 group naming policy considerations
3.5 Create groups in Exchange Online and SharePoint Online
3.5.1 Creating groups in Exchange Online
3.5.2 Creating Security Groups in SharePoint Online
3.5.3 FAQ About SharePoint Security Group
4. Custom Domain
4.1 Plan a custom domain for your Microsoft 365 deployment
4.1.1 Multiple domains
4.1.2 Subdomains
4.1.3 Domain numbers
4.1.4 Domain adding order
4.1.5 DNS record hosting
4.1.6 Access to the DNS console
4.1.7 Not registering DNS
4.1.8 Not changing all records
4.2 DNS zones for a custom domain
4.3 Configuring Custom Domain Name for Microsoft 365
4.3.1 DNS Zone planning in a hybrid deployment
4.3.2 DNS zone planning for a custom domain
4.3.3 Internal DNS zones and external DNS zones have different names
4.3.4 Split DNS
4.3.5 DNS zone planning when moving an entire tenant to the cloud
4.4 DNS record requirements for a Custom Domain
4.4.1 External DNS records required for Microsoft 365 (core services)
4.4.2 External DNS records required for email in Microsoft 365 (Exchange Online)
4.4.3 External DNS records required for Microsoft Teams
4.4.4 External DNS records required for Microsoft 365 Single Sign-on
4.4.5 External DNS records required for Sender policy framework (SPF)
5. Configure Client Connectivity to Microsoft 365
5.1 how automatic client configuration works
5.2 DNS records required for client configuration
5.3 Configure Outlook clients
5.3.1 Connectivity protocols
5.3.2 Outlook connectivity for cloud-only and hybrid deployments
5.3.3 Network configuration
5.4 Troubleshooting client connectivity
5.4.1 Microsoft Remote Connectivity Analyzer
5.4.2 Microsoft 365 Support and Recovery Assistant
6. Administrative Roles in Microsoft 365
6.1 Microsoft 365 permission model
6.1.1 Microsoft 365 admin center
6.1.2 Microsoft Defender portal
6.1.3 Microsoft Purview compliance portal
6.1.4 Administrator roles
6.1.5 Relationship of members, roles, and role groups
6.1.6 Types of roles and role groups in Microsoft 365
6.2 Microsoft 365 admin roles
6.2.1 Security guidelines for assigning roles
6.2.2 Commonly used Microsoft 365 admin center roles
6.3 Assign admin roles to users in Microsoft 365
6.4 Manage permissions using administrative units in Microsoft Entra ID
6.4.1 Deployment scenario
6.4.2 License requirements
6.4.3 Manage administrative units
6.4.4 Currently supported scenarios
6.4.5 Managing permissions in administrative units
6.5 Azure AD (or Entra ID) Priviliged Identiy Management
6.5.1 Enabling Azure AD (or Entra ID) Privileged Identity Management
6.5.2 Assigning Azure Resource Roles in PIM
6.5.3 Activating an Eligible resource role in Azure AD (or Entra ID) PIM
6.6 Best practices when configuring administrative roles
6.6.1 Manage to least privilege
6.6.2 Use Privileged Identity Management to grant just-in-time access
6.6.3 Turn on multifactor authentication for all your administrator accounts
6.6.4 Configure recurring access reviews to revoke unneeded permissions over time
6.6.5 Limit the number of Global Administrators to less than five
6.6.6 Use groups for Microsoft Entra role assignments and delegate the role assignment
6.6.7 Use cloud native accounts for Microsoft Entra roles
7. Tenant health and services in Microsoft 365
7.1 Monitor the health of your Microsoft 365 services
7.1.1 Microsoft 365 Health dashboard
7.1.2 Critical alerts
7.2 Monitor tenant health using Microsoft 365 Adoption Score
7.2.1 Adoption Score prerequisites
7.2.2 How the Adoption Score is calculated
7.2.3 Category details pages
7.2.4 Group level aggregates
7.2.5 Organizational messages
7.3 Implement Microsoft 365 Network Connectivity Assessments and Insights
7.3.1 Prerequisites for network connectivity assessments to appear
7.3.2 Option 1 - Turn on your location opt-in setting to automatically collect data from devices using Windows Location Services
7.3.3 Enable Windows Location Services
7.3.4 Add locations and provide LAN subnet information
7.3.5 Option 2 - Go to your Locations list to manually add or upload location data
7.3.6 Option 3 - Run the Microsoft 365 network connectivity test from your office locations
7.3.7 Interpret network assessments
7.3.8 How do I use this information?
7.3.9 Enterprise network connectivity challenges
7.3.10 Microsoft 365 Network Insights
7.4 More about Microsoft 365 Backup (Preview)
7.4.1 Microsoft and partner offerings
7.4.2 Microsoft 365 Backup pricing model
7.4.3 Pricing calculator
7.4.4 Microsoft 365 Backup architecture
7.4.5 Backup policy performance
7.4.6 Restoration performance
7.5 Develop an incident response plan
7.6 Requesting assistance from Microsoft
7.6.1 Administrator role and responsibilities
8. Microsoft 365 Apps for Enterprise
8.1 Self-service installation of Microsoft 365 Apps for enterprise
8.1.1 Obstacles to a successful self-service installation of Microsoft 365 Apps for enterprise
8.1.2 Prohibit all users from installing Microsoft 365 Apps for enterprise
8.2 Deploy Microsoft 365 Apps for enterprise from the cloud
8.2.1 The Office Content Delivery Network
8.2.2 The Office Deployment Tool
8.3 Deploy Microsoft 365 Apps for enterprise from a local source
8.4 Manage updates to Microsoft 365 Apps for enterprise
8.4.1 Update options
8.4.2 Using the Office Deployment Tool's configuration.xml file to manage updates
8.5 Update channels for Microsoft 365 Apps for enterprise
8.5.1 Current Channel
8.5.2 Current Channel (Preview)
8.5.3 Monthly Enterprise Channel
8.5.4 Semi-Annual Enterprise Channel
8.5.5 Channel recommendations
8.5.6 Configuring users for update channels
8.6 Manage your cloud apps using the Microsoft 365 Apps admin center
8.6.1 Office cloud policy service
8.6.2 Office Inventory
8.6.3 Service update status
9. Analyze your Microsoft 365 workplace data using Microsoft Viva Insights
9.1 Analytical features of Microsoft Viva Insights
9.1.1 Privacy and data protection
9.1.2 Role descriptions and access levels
9.2 Explore Personal insights
9.2.1 Personal insights data
9.2.2 Data privacy concerning Personal insights data
9.3 Team insights
9.3.1 About team data and data privacy
9.3.2 Permissions and app setup
9.4 Organization insights
9.4.1 Insights by role
9.4.2 Using Organization insights
9.4.3 Organization insights per tab
10. Identity Synchronization
10.1 Authentication options for the hybrid identity model
10.1.1 Password hash synchronization (PHS)
10.1.2 Pass-through authentication (PTA)
10.1.3 Federated authentication
10.2 Explore directory synchronization
10.3 Prepare for directory synchronization
10.3.1 Source of authority
10.3.2 Active Directory cleanup
10.3.3 UPN suffixes
10.3.4 Microsoft 365 IdFix tool
10.4 Comparing Directory Synchronization tools
10.4.1 Microsoft Entra Connect Sync
10.4.2 Microsoft Entra Cloud Sync
10.4.3 Comparison between Microsoft Entra Connect Sync and Microsoft Entra Cloud Sync
10.4.4 Microsoft Entra Connect Sync server
10.4.5 SQL Server used by Microsoft Entra Connect Sync
10.4.6 Accounts
10.4.7 Connectivity
10.4.8 Outbound proxy server requirements
10.4.9 Hardware requirements for Microsoft Entra Connect Sync
10.5 Configuring Microsoft Entra Connect Sync with Express Setup
10.6 Microsoft Entra Connect Sync Custom setup
10.7 Monitoring AD Connect Synchronization Health
10.7.1 Microsoft Entra Connect Sync Insight
10.7.2 Sync Latency
10.7.3 Sync Object Changes
11. Managing Syncrhonized Identities
11.1 Manage users with directory synchronization
11.1.1 Managing user accounts
11.1.2 Recovering an accidentally deleted user account
11.1.3 Recovering from unsynchronized deletes
11.1.4 Moving an out-of-sync user
11.1.5 Enhanced user management
11.1.6 Enable password writeback for SSPR
11.1.7 Device writeback
11.2 Manage groups with directory synchronization
11.2.1 Group writeback in Microsoft Entra Connect Sync
11.3 Maintain directory synchronization using Microsoft Entra Connect Sync security groups
11.4 Configure object filters for directory synchronization
11.4.1 Disable the scheduled task
11.4.2 Configuring OU-based filtering
11.4.3 Apply and verify changes
11.5 About Microsoft Identity Manager
11.5.1 Key features of Microsoft Identity Manager
11.5.2 How is MIM commonly used?
11.6 Troubleshoot directory synchronization
11.6.1 Deactivate and reactivate directory synchronization
11.6.2 Identity synchronization and duplicate attribute resiliency
11.6.3 View directory synchronization errors in the Microsoft 365 admin center
11.6.4 Unhealthy identity synchronization notification
11.6.5 Directory synchronization troubleshooter
11.6.6 Synchronization Service Manager
11.6.7 Troubleshoot password hash synchronization with Microsoft Entra Connect Sync
12. Email Protection with Defender XDR
12.1 Anti-malware policies
12.1.1 Anti-malware policies in EOP
12.1.2 The anti-malware pipeline
12.1.3 Create anti-malware policies in the Microsoft Defender portal
12.1.4 Zero-hour auto purge (ZAP)
12.2 Anti-spam policies
12.2.1 Allowlists and blocklists in anti-spam policies
12.3 EOP Anti-Spoofing Protection
12.3.1 How spoofing works in phishing attacks
12.3.2 Different types of spoofing
12.3.3 Problems with anti-spoofing protection
12.4 Protect users from malicious attachments by using Safe Attachments
12.5 Safe Links
12.6 URL detonation
12.6.1 Suspicious message warning
13. Purview Data Loss Prevention
14. Purview Insider Risk Management
14.1 Introduction to Insider Risk Management
14.2 Risk Pain Points in the Modern Workplace
14.3 Common insider risk scenarios
14.4 Insider risk management workflow
14.5 Concepts of Insider Risk Policies
14.5.1 Components of a policy
14.5.2 Policy dashboard
14.5.3 Policy templates
14.5.4 Insider Risk Management General settings
14.5.5 Policy Indicators
14.5.6 Policy timeframes
14.5.7 Intelligent detections
14.6 Create and manage insider risk policies
14.6.1 Required roles or permissions to manage Insider Risk Policies
14.6.2 Potential dependencies
15. Purview Retention Labels and Policies
15.1 An Introduction to Data Lifecycle Management
15.2 Retention policy precedence
15.3 Configure retention labels
15.4 Configure manual retention label policies
 付款。
付款。