(在家觀看 = 0%,在校觀看 = 100%)
100% 在校觀看日期及時間:
自由選擇,點選以下地區觀看辦公時間及位置
課時: 30 小時
享用時期: 15 星期。進度由您控制,可快可慢。
課堂錄影導師:Franco
在校免費試睇:首 3 小時,請致電以上地點與本中心職員預約。
本課程提供在校免費重睇及導師解答服務。
(在家觀看 = 30%,在校觀看 = 70%)
30% 在家觀看日期及時間:
每天 24 小時全天候不限次數地觀看
70% 在校觀看日期及時間:
本中心辦公時間內自由選擇,點選以下地區觀看辦公時間及位置
旺角:$5,980 報名 phone

電話:2332-6544
觀塘:$5,980 報名 phone

電話:3563-8425
北角:$5,980 報名 phone

電話:3580-1893
沙田:$5,980 報名 phone

電話:2151-9360
課時: 30 小時
在家及在校觀看: 在家觀看首 9 小時,在校觀看尾 21 小時。
享用時期: 15 星期。進度由您控制,可快可慢。
課堂錄影導師:Franco
在校免費試睇:首 3 小時,請致電以上地點與本中心職員預約。
本課程提供在校免費重睇及導師解答服務。
雲端運算 (Cloud Computing) 提供一種簡單的方式,透過互聯網、VPN (Virtual Private Network) 等的方式存取雲端伺服器、儲存、資料庫和各種應用程式服務。它有以下的好處:
- 不用花費大筆金錢來建立、執行和維護自已的資料中心 (Data Center)。
- 大多數的雲端運算服務是按用量收費,可大可小,可多可少。從此不用再估算容量,方便靈活。
- 符合或取得多個合規要求,例如 ISO 9001 (全球品質標準)、ISO 27001 (安全管理控制)、ISO 27017 (雲端特定控制)、ISO 27018 (個人資料保護)、PCI DSS 第 1 級 (支付卡標準,第 1 級表示每年儲存、處理和 / 或傳輸超過 30 萬筆交易的任何服務提供者)、SOC 1 (稽核控制報告)、SOC 2 (安全性、可用性和機密性報告)、SOC 3 (一般控制報告)、C5 (https://aws.amazon.com/compliance/bsi-c5/) 等。詳情可以參閱 https://aws.amazon.com/compliance/pci-data-privacy-protection-hipaa-soc-fedramp-faqs/
- 大量成功的商業例子及經驗。
現時有不少公司提供雲端運算 (Cloud Computing) 服務,Amazon Web Service (AWS) 被 Gartner* 評為全球第一的 Cloud Infrastructure as a Service。
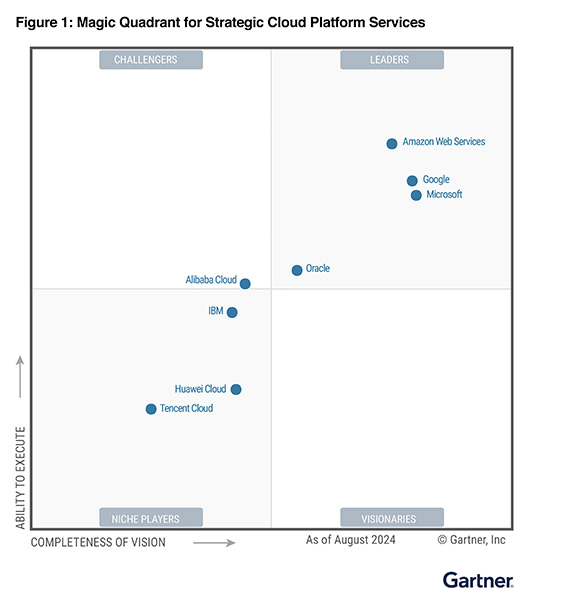
“Magic Quadrant for Strategic Cloud Platform Services”
* Gartner 是知名的信息技術研究和顧問的美國上市公司。
為了你有知識和能力使用 AWS 技術以構建和部署安全可靠的服務,AWS 便推出 AWS Certified Solutions Architect – Associate 國際認可證書。本中心的 AWS Certified Solutions Architect – Associate 國際認可證書課程由 Franco Tsang 籌備多時,精心編排。由上堂、溫習、考試研習、做試題至最後考試,均為你度身訂造,作出有系統的編排。務求真正教識你,又令你考試及格。
以下是本課程內容簡介:
1. Regions, Availability Zones (AZ) and Local Zone |
本課程緊貼時代需要,相關的概念 / 內容 / 產品能被應用到不同的情景中,例如:
- 爆 hard disk,唔 delete files 唔熄機地擴大 C drive:
https://www.facebook.com/systematic.hk/photos/a.173134451964/1015... [圖] - 程式用 AWS SNS sends 短訊 (Amazon SNS):
https://www.facebook.com/systematic.hk/photos/a.173134451964/1015... [圖] - 在 AWS 上分析情歌歌詞的情感 (Sentiment Analysis):
https://www.facebook.com/systematic.hk/photos/a.173134451964/1015... [圖] - 在 AWS 上玩 Hadoop Big data analysis (Amazon EMR + Amazon S3):
https://www.facebook.com/systematic.hk/photos/a.173134451964/1015... [圖] - 在 AWS 使用 Check Point R80.30 實踐 SSL VPN / TLS VPN (以手機 App 接駁 (Check Point Capsule Connect)) (Amazon EC2 + VPC):
https://www.facebook.com/systematic.hk/photos/a.173134451964/1015... [圖] - 更多應用情景 / 導師在 Facebook 所分享的文章:
https://www.systematic.com.hk/course_Franco.htm?panel=2
| 課程名稱: |
AWS Certified Solutions Architect - Associate (Amazon Cloud AWS SAA) 國際認可證書課程 - 簡稱:Amazon Cloud AWS SAA Training Course |
| 課程時數: | 課堂 30 小時 (共 10 堂) |
| 適合人士: | 對雲端運算 (Cloud Computing) 技術有興趣的人士 |
| 授課語言: | 以廣東話為主,輔以英語 |
| 課程筆記: | 本中心導師親自編寫英文為主筆記,而部份英文字附有中文對照。 |
| 提供模擬考試題目: | 本中心為學員提供模擬考試題目,每條考試題目均附有標準答案。 |
只要你於下列科目取得合格成績,便可獲 AWS 頒發 AWS Certified Solutions Architect - Associate 國際認可證書:
| 考試編號 | 考試名稱 |
| SAA-C03 | AWS Certified Solutions Architect - Associate |
本中心為 VUE 指定的 AWS Certified Solutions Architect - Associate 考試試場,導師會在課堂上講解考試程序。考試費為 USD $150。
|
課程名稱:AWS Certified Solutions Architect - Associate (Amazon Cloud AWS SAA) 國際認可證書課程 - 簡稱:Amazon Cloud AWS SAA Training Course |
儘管 AWS Certified Solutions Architect – Associate 考試理論色彩比較濃厚,但導師仍然會以示範為主導的方式教授這課程,令同學可以實在一點學習 / 享受 AWS 技術。
- 第 1 部份:背景知識,例如 Regions and Availability Zones 等。
- 第 2 部份:EC2 (Elastic Compute Cloud) 和 EBS (Elastic Block Store) 。本章節主要教授如何操作 EC2 instances (可以粗略地理解為 Virtual Machines) 及 EBS (可以粗略地理解為 instance 的 hard disk) ,而在課堂上會有準確的解釋。
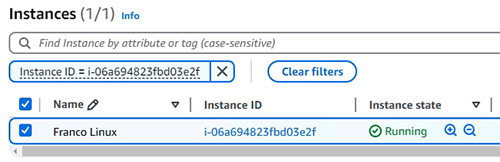
- 新增 EC2 instances (Linux 和 Windows Server) 並了解其相關的知識,例如 AMI、Instance Types、User data (示範使用如何 Shell Scripting 及 PowerShell)、Storage、Tags、Security Groups、Key Pairs、接駁 instances 等概念
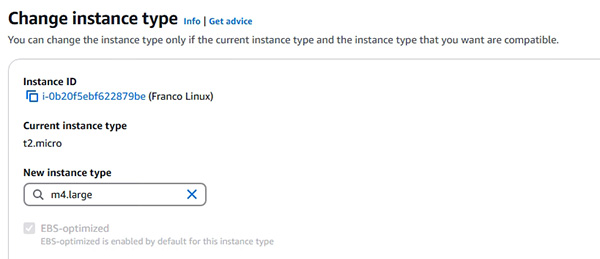
- 改變 EC2 instances 的 instance types (示範由少 RAM 的 instance types 變為多 RAM 的 instance types)
- 了解 On-demand、Reserved Instances、Dedicated Hosts、Spot Instances 的特點 (教授如何以節省 90% 的費用使用 EC2)
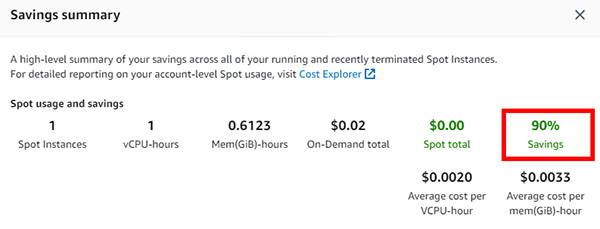
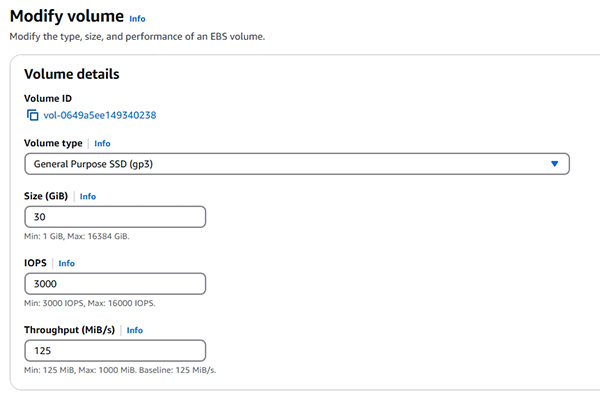
- Instance Store、Encrypted / Unencrypted volumes (示範新增 Encrypted EBS 及擴大 EBS 的容量,例如 1G → 2G)
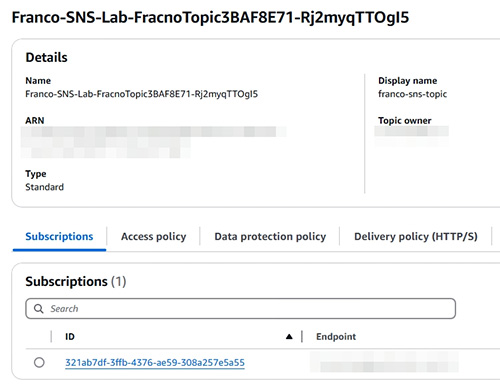
- 第 3 部份:CloudWatch 和 SNS (Simple Notification Service)。本章節主要教授如何監控 Cloud Infrastructure。

- 新增 SNS topics 和 subscriptions
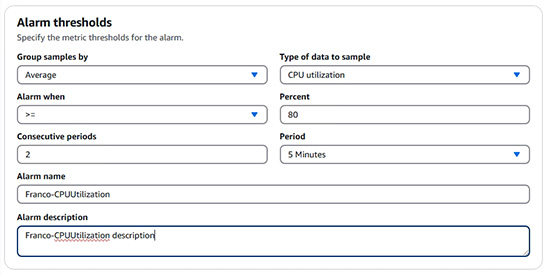
- CloudWatch Alarm (示範如何建立 CloudWatch Alarm,如果 CPU Utilization 過高就 send email 給 Franco)。
- CloudWatch Metric (示範如何操作 CloudWatch Metric)。
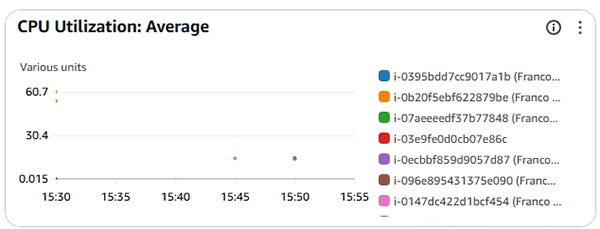
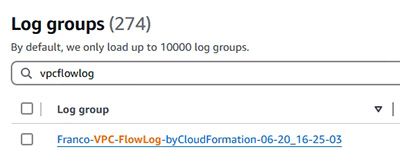
- CloudWatch Log (示範如何操作 CloudWatch Log) 。
- 預設 CloudWatch 不能監察 Instance 的 memory,究竟如何監察 Instance 的 memory? 導師會在課堂上教授監察 Instance memory 的技巧。
- 其他理論性質的知識及細項技術 。
- 第 4 部份:VPC (Virtual Private Cloud) 和VPN。本章節主要教授如何設定 Cloud networking 及架設 VPN (virtual private network) + BGP (Border Gateway Protocol) 以進行連接 “天和地 (AWS VPC 及 企業內部網絡)” 。
- VPC、NACL 及 Security Groups (示範如何建立 VPC) 。
- Public Subnets 、Internet gateway 及 public route table (示範如何建立 Public Subnet) 。
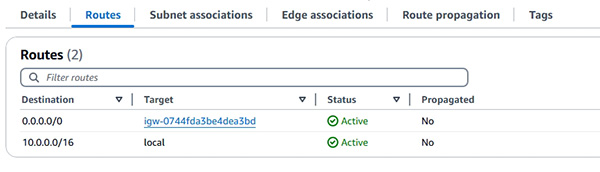
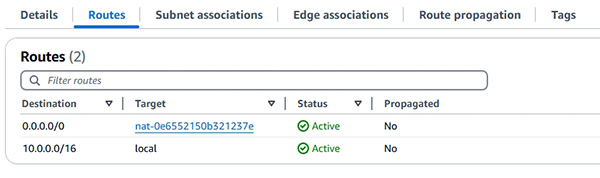
- Private Subnets 、NAT gateway 及 private route table (示範如何建立 Private Subnet) 。
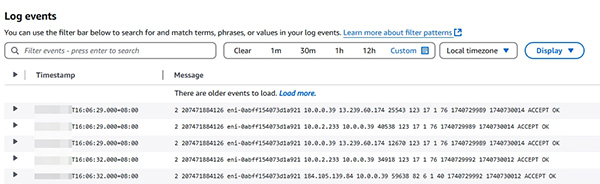
- Flow log (示範如何取得 Flow log) 。
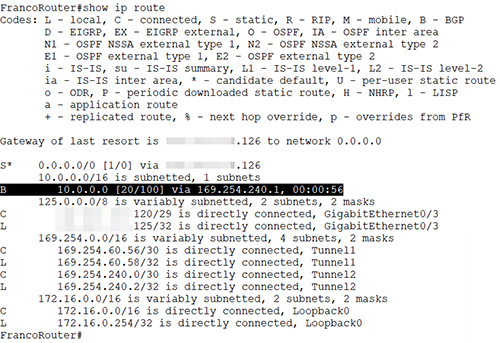
- 架設 VPN 以將企業內部網絡接駁到 AWS VPC 內 (示範以 Cisco router架設 VPN 到 AWS)。
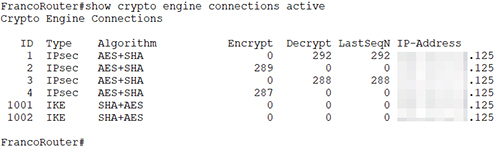
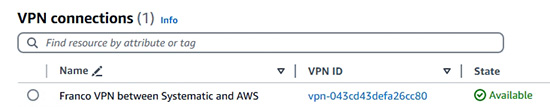
- 使用 BGP 交換路由資料。
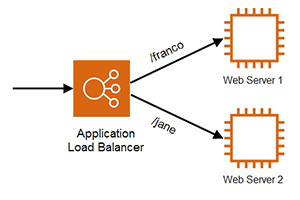
- 第 5 部份:ELB (Elastic Load Balancing) 和 Auto Scaling。本章節主要教授 AWS 的負載平衡和動態擴展縮減方案 。

- Elastic Load Balancing 概念
- Application Load Balancing (示範如何實踐 Application Load Balancing with path listener)
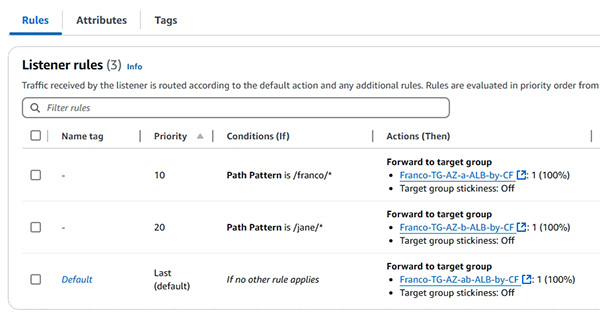
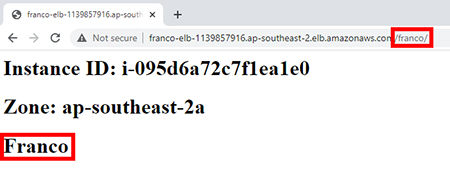
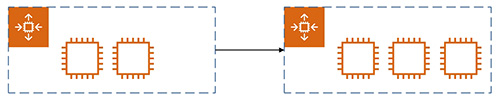
- Manual Scaling (示範 Manual Scaling 由 2 個 instances 擴展到 3 個 instances)
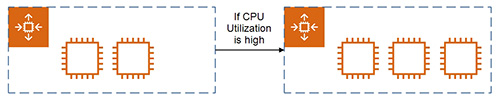
- Auto Scaling (示範如果 CPU Utilization 過高,就會由 2 個 instances 擴展至 CPU Utilization 下降到一個理想的水平)
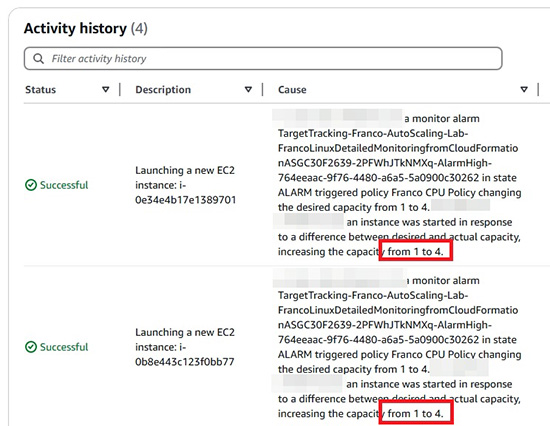
- 其他理論性質的知識及細項技術 。
- 第 6 部份:S3、Glacier 和 Storage Gateway。本章節主要教授 AWS 的儲存方案 。

- S3 bucket (示範新增 S3 bucket 以儲存檔案)
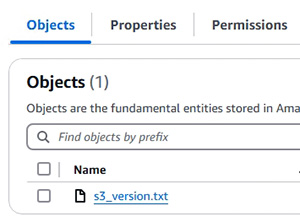
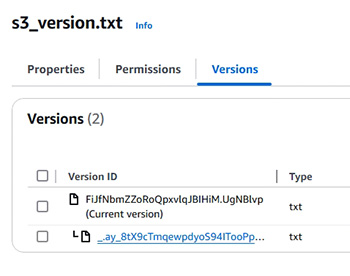
- S3 versioning (示範在 S3 內實踐版本控制)
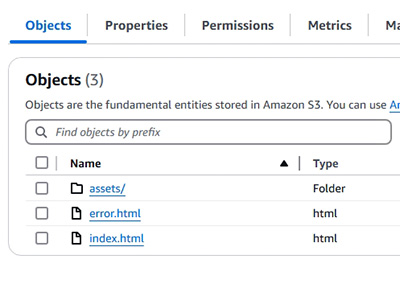
- S3 web host 並了解其限制 (使用 S3 以寄存網頁)

- 教授 FSx 相關的技術
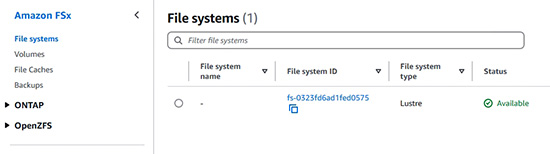
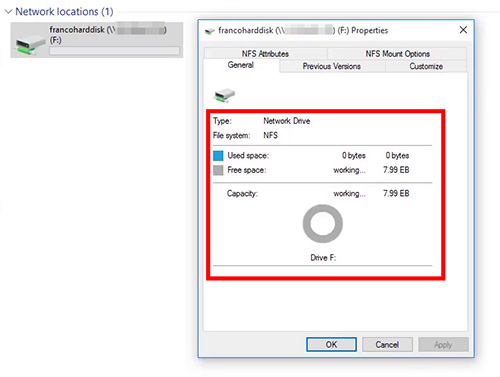
- 導師會在課堂教授一種有趣的技術令大家 “在地” 的 Windows 或 Linux 有 “7.99 EB” 的儲存空間。其實真實的儲存空間是不是 7.99 EB 呢?導師在課堂再詳談當中的故事。
- 其他理論性質的知識及細項技術 ,例如權限等。
- 第 7 部份:RDS (Relational Database Service) 、Dynamo DB 和 ElastiCache。本章節主要教授 AWS 的 database 及 caching 方案。

- 在EC2內安裝 database 還是使用 RDS?
- 新增 RDS (示範新增 Multi-AZ RDS (writer and reader))
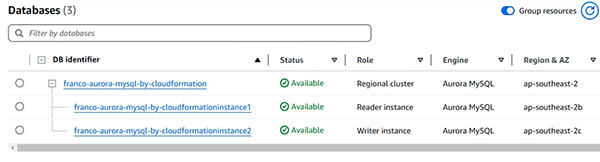
- DB Snapshot 及其作用 (示範建立及使用 DB Snapshot)
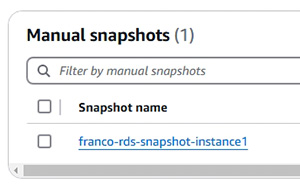
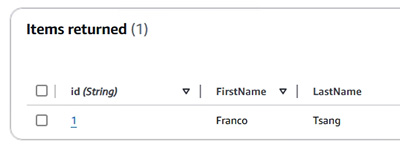
- DynamoDB 的特色及其操作 (示範建立及使用 DynamoDB)
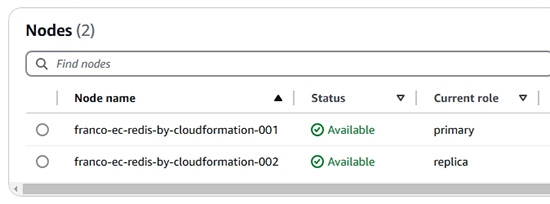
- ElastiCache 的特色及其操作 (示範建立及使用 ElastiCache: Redis)
- 其他理論性質的知識及細項技術
- 第 8 部份:Route 53。本章節主要教授 AWS 的 DNS 方案。
- 在 Route 53 內使用現有的 domains (無需在 AWS 內購買 domains)
- Hosted Zones (示範建立 Hosted Zones以開始管理 domains)
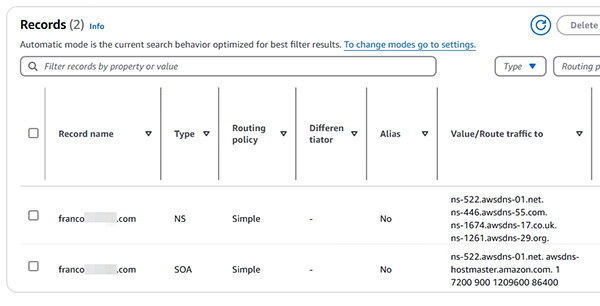
- 示範按比例進行 DNS name resolution
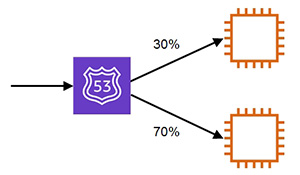
- 示範按地區進行 DNS name resolution
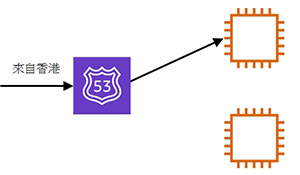
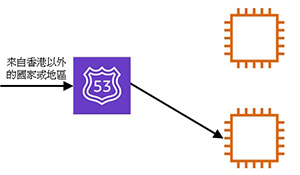
- 示範按 latency 進行 DNS name resolution
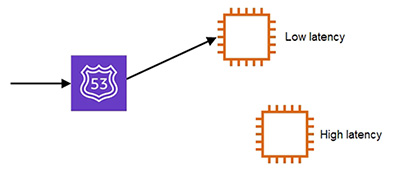
- 示範按 failover (示範 failover policy)
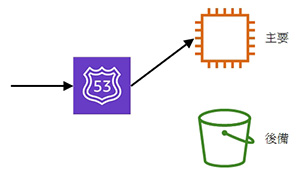
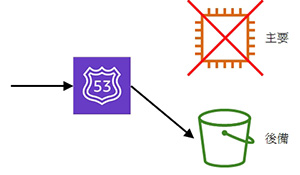
- 其他理論性質的知識及細項技術,例如 Record Types 等
- 第 9 部份:CloudFront。本章節主要教授 AWS 的 CDN (Content Delivery Network) 方案。
- 教授CDN (Content Delivery Network) 的技術概念,甚麼場合適合使用 CDN

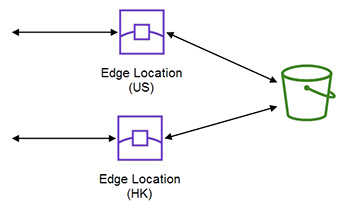
- 示範建立 CloudFront
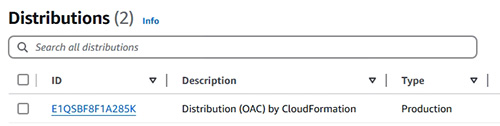
- 教授使用 Origin Access Control (OAC) 進行存取控制 (Access Control)
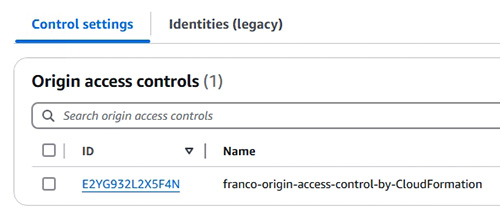
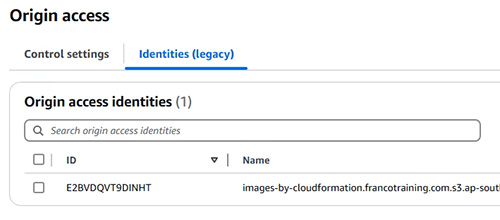
- 教授使用 Origin Access Identity (OAI) 進行存取控制 (Access Control)
- 第 10 部份:SQS (Simple Queue Service) 、API Gateway 和 Lambda。本章節主要教授 AWS message queue、應用程式後端服務及無伺服器應用程式方案。

- 教授 message queue、應用程式後端服務及無伺服器應用程式的技術概念,甚麼場合適合使用它們
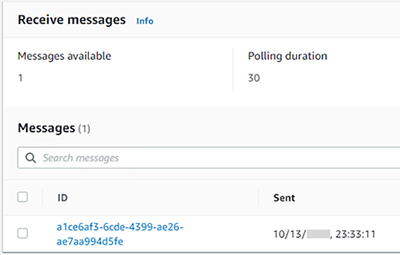
- 示範使用 SQS
- 示範使用 API Gateway
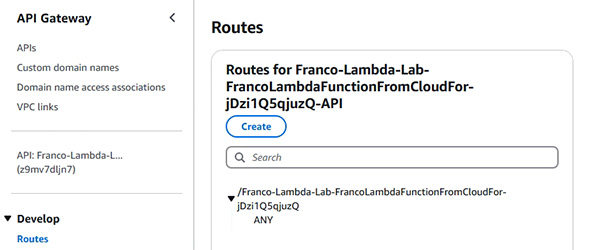
- 示範以 Node.js 作為程式語言使用 Lambda
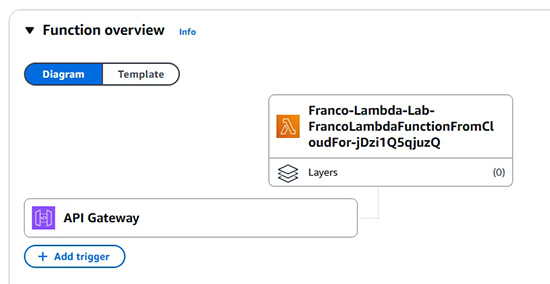
- 其他理論性質的知識及細項技術
- 第 11 部份:IAM (Identity and Access Management) 。本章節主要教授如何安全地管理對 AWS 服務和資源的存取。

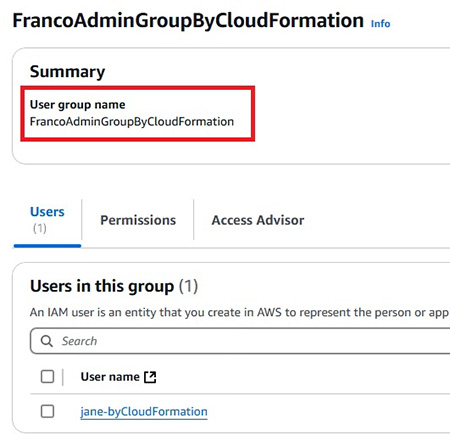
- 示範新增 Administrators
- 示範 MFA (Multi-Factor Authentication)

- 新增 Policy 並限制某些用戶不能 stop production 的 instances。
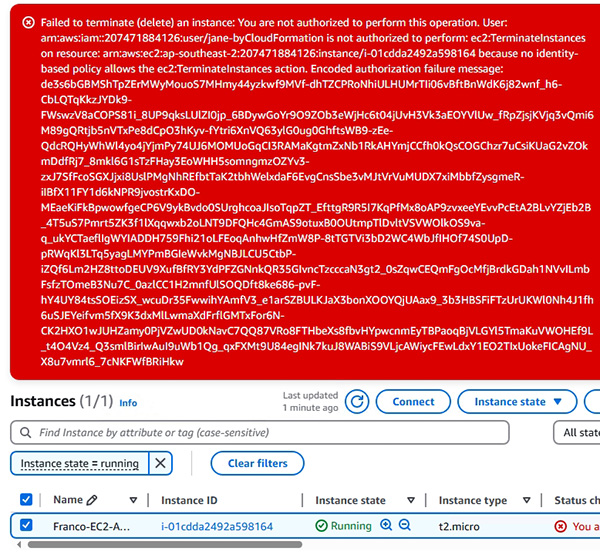
- 其他理論性質的知識及細項技術
- 第 12 部份:Miscellaneous 。本章節主要教授其他 AWS 的概念和技術,例如 DataSync、CloudTrail、Athena、WAF、Secrets Manager、Inspector、Macie、GuardDuty 等
The course content above may change at any time without notice in order to better reflect the content of the examination.
1 Regions, Availability Zones (AZ), Local Zone and Wavelength Zones
1.1 Regions
1.2 Availability Zones (AZ)
1.3 Local Zone
1.4 Wavelength Zones
2 Amazon Elastic Compute Cloud (Amazon EC2)
2.1 Introduction to Amazon EC2
2.2 Amazon Machine Images (AMI)
2.2.1 AWS Marketplace
2.3 Instance store (Ephemeral) vs Amazon Elastic Block Store (Amazon EBS)
2.3.1 Instance store (Ephemeral)
2.3.2 Amazon Elastic Block Store (Amazon EBS)
2.4 Instance types
2.4.1 T3 / T2
2.4.1.1 CPU Credits and Baseline Performance
2.4.1.1.1 One CPU credit (Spending CPU Credits)
2.4.1.1.2 Earning CPU Credits
2.4.1.1.3 CPU Credits Monitoring
2.5 On-Demand Instances, Reserved Instances (RI) and Spot Instances
2.5.1 On-Demand instances
2.5.2 Reserved instances (RI)
2.5.3 Spot instances
2.5.4 Dedicated hosts and dedicated instances
2.5.4.1 Dedicated hosts
2.5.4.2 Dedicated instances
2.6 Network and Security
2.6.1 Network
2.6.1.1 Network speed and placement group
2.6.1.2 IP addresses
2.6.1.2.1 Elastic IP addresses (EIP)
2.6.2 Security
2.6.2.1 Key Pairs
2.6.2.2 Security Groups
2.6.2.2.1 Rules of Security Groups
2.7 Pricing
2.7.1 "Charging items"
2.8 Demonstration: Launch and connect to a Linux instance
2.8.2 Demonstration: Choose AMI (Amazon Machine Image)
2.8.3 Demonstration: Choose instance types
2.8.4 Demonstration: Create Key pair
2.8.5 Demonstration: Convert private key from pem to ppk (Optional)
2.8.6 Demonstration: Network settings and Security Group
2.8.7 Demonstration: Configure Storage
2.8.8 Demonstration: Advanced details / user data
2.8.9 Demonstration: Launch instance
2.8.10 Demonstration: Connect to a Linux instance (CLI) via EC2 Instance Connect (EC2 Instance Connect)
2.8.11 Demonstration: Connect to a Linux instance (CLI) via PuTTY
2.8.12 Demonstration: Connect to a Linux instance (File transfer)
2.8.13 Demonstration: "user-data" verification
2.9 Instance metadata
2.9.1 Demonstration: Instance metadata (General)
2.9.2 Demonstration: Instance metadata (local-ipv4)
2.9.3 Demonstration: Instance metadata (public-ipv4)
2.10 Demonstration: Stop, change instance type and start an instance
2.10.1 Demonstration: Stop an instance
2.10.2 Change instance type and start an instance
2.11 Demonstration: Screenshot
2.12 Launch more like this
2.12.1 Demonstration: Launch more like this
2.13 Terminate an instance
2.13.1 Demonstration: Terminate an instance
2.14 Custom AMIs (Amazon Machine Images)
2.14.1 Demonstration: Create a custom AMI (Amazon Machine Images)
2.14.2 Demonstration: Create an instance based on a custom AMI
2.14.3 Demonstration: Deregister an AMI
2.15 Demonstration: Windows instances (Windows Server)
2.16 Demonstration: From ppk to pem
2.17 Demonstration: Decrypt the password and connect to EC2 Windows instance
2.18 Spot instances
2.18.1 Demonstration: Create a spot instance
2.18.2 Demonstration: Terminate a spot instance
3 AWS Command Line Interface (AWS CLI)
3.1 Install AWS CLI
3.1.1 Demonstration: Install AWS CLI in Windows
3.2 Access key ID and Secret access key
3.2.1 Demonstration: Generate Access key ID and Secret access key
3.3 Using AWS CLI
3.3.1 Demonstration: "Login" to AWS CLI and list out all regions
3.3.2 Demonstration: JSON format vs table format
4 Amazon Elastic Block Store (Amazon EBS)
4.1 Introduction to Amazon EBS
4.2 Volume types (io1, io2, io2 Block Express, gp2, gp3, st1 and sc1)
4.3 Snapshot
4.3.1 Fast Snapshot Restore (FSR)
4.4 Encryption
4.5 Amazon EBS - optimized instances
4.6 Demonstration: "View" Instance store (Ephemeral)
4.7 Demonstration: Create EBS volumes
4.8 Demonstration: Attach EBS volumes
4.9 Demonstration: Use the newly created EBS volumes
4.10 Demonstration: Resize the volumes
4.11 Demonstration: Creating snapshot from volume
4.12 Demonstration: Exploring "copy snapshot"
4.13 Demonstration: Detach and delete volumes, snapshots and EC2 instances
5 Amazon CloudWatch and Amazon Simple Notification Service (Amazon SNS)
5.1 Amazon CloudWatch
5.1.1 Introduction to CloudWatch
5.1.2 Metrics
5.1.2.1 Basic and Detailed Monitoring
5.1.2.1.1 Basic Monitoring
5.1.2.1.2 Detailed Monitoring
5.1.2.2 Custom Metrics and sharing CloudWatch dashboards
5.1.3 Logs
5.1.4 Alarms
5.1.5 CloudWatch Events / Amazon EventBridge
5.2 Amazon Simple Notification Service (SNS)
5.2.1 Introduction to SNS
5.2.2 Characteristics of SNS
5.3 Demonstration: CloudWatch in EC2 instances and SNS
5.3.1 Demonstration: Create a SNS topic and subscription
5.3.2 Demonstration: Basic Monitoring of EC2 instances
5.3.3 Demonstration: Alarms of EC2 instances
5.3.4 Demonstration: Delete alarms, SNS topics and SNS subscriptions.
5.3.5 Demonstration: Detailed Monitoring
5.3.6 Monitor EC2 instances' memory (Custom metrics) with EC2 instance profile
5.3.6.1 Background of EC2 instance profile
5.3.6.2 Background of EC2 memory monitoring
5.3.6.3 Demonstration: Monitor EC2 instances' memory (Custom metrics) with EC2 instance profiles (IAM roles)
5.3.6.3.1 Demonstration: Create an IAM role
5.3.6.3.2 Demonstration: Create an EC2 instance with instance profiles (IAM roles)
5.3.6.3.3 Demonstration: Install CloudWatch Agent
5.3.6.3.4 Demonstration: Monitor EC2 instances' memory (Custom metrics)
5.3.6.3.5 Demonstration: Delete EC2 instances, IAM roles and inline policies
6 Virtual Private Cloud (VPC) [with Elastic IP (EIP), Elastic Network Interface (ENI), Network Address Translation (NAT) and Virtual Private Network (VPN)]
6.1 Introduction to Virtual Private Cloud (VPC)
6.2 Pricing
6.3 Common VPC designs
6.3.1 VPC with a single public subnet
6.3.2 VPC with public and private subnets
6.3.3 VPC with public subnets, private subnets and VPN access
6.3.4 VPC with a private subnet only and VPN access
6.4 Create VPC, Edit DNS Resolution and Edit DNS Hostnames
6.4.1 Demonstration: Create VPC, Edit DNS Resolution and Edit DNS Hostnames
6.5 Security Groups in a VPC
6.5.1 Demonstration: Security Groups in a VPC
6.6 Subnets and Routing
6.6.1 Introduction to subnet concepts
6.6.1.1 Subnets
6.6.1.2 Public subnets
6.6.1.3 Private subnets
6.6.2 Introduction to routing concepts in VPC
6.6.2.1 Route tables
6.6.2.2 Main route tables / Default route table
6.6.3 Demonstration: Public Subnets
6.6.3.1 Internet Gateway (IGW)
6.6.3.2 Demonstration: Create an internet gateway and attach to a VPC
6.6.3.3 Demonstration: Create a subnet
6.6.3.4 Demonstration: Create a route table and associate to a public subnet (internet gateway, igw)
6.6.3.5 Demonstration: Create an EC2 instance in a public subnet
6.6.4 Demonstration: Private Subnets
6.6.4.1 Demonstration: Create a subnet
6.6.4.2 Demonstration: Create an EC2 instance with a custom ENI (Elastic Network Interface) with private IP
6.6.4.2.1 Elastic Network Interface (ENI)
6.6.4.2.2 Demonstration: Create a custom ENI (Elastic Network Interface) with private IP
6.6.4.2.3 Demonstration: Create an EC2 instance with a custom ENI (Elastic Network Interface)
6.6.4.3 Demonstration: Connect to private subnet instance from public subnet instance
6.6.4.4 Demonstration: NAT gateway (ngw), route tables and Elastic IP (EIP)
6.6.4.4.1 Demonstration: Allocate an Elastic IP (EIP)
6.6.4.4.2 Demonstration: Create a NAT gateway (ngw)
6.6.4.4.3 Demonstration: Prepare a route table and use NAT gateway (ngw)
6.6.4.4.4 Demonstration: Delete NAT gateway (ngw) and release Elastic IP (EIP)
6.7 Network Access Control Lists (NACLs)
6.7.1 Introduction to Network Access Control Lists (NACLs)
6.7.2 Demonstration: Network Access Control Lists (NACLs)
6.7.3 Comparison of security group and network ACL (NACL)
6.8 VPC Flow Logs
6.8.1 Demonstration: VPC Flow Logs
6.8.1.1 Demonstration: Create CloudWatch log group
6.8.1.2 Demonstration: Create IAM Role with "assume role" concepts
6.8.1.3 Demonstration: Create VPC flow log
6.8.2 Demonstration: Delete VPC Flow Logs, IAM role and Log Group
6.8.2.1 Demonstration: Delete VPC Flow Logs
6.8.2.2 Demonstration: Delete IAM role
6.8.2.3 Demonstration: Delete Log Group
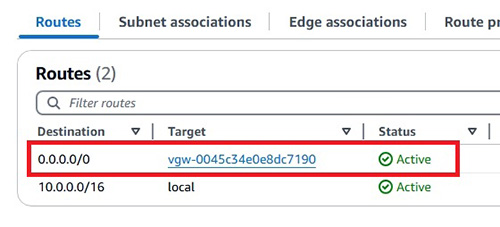
6.9 Virtual Private Network (VPN) and Border Gateway Protocol (BGP)
6.9.1 Introduction to Virtual Private Network (VPN)
6.9.2 Introduction to Border Gateway Protocol (BGP)
6.9.3 Demonstration: Connect on-premise infrastructure to AWS VPC
6.9.3.1 Demonstration: Prepare a customer gateway (Cisco Routers)
6.9.3.2 Demonstration: Create Customer Gateway in VPC (cgw)
6.9.3.3 Demonstration: Create Virtual Private Gateway (vgw) and attach Virtual Private Gateway to a VPC
6.9.3.4 Demonstration: Create a VPN connection in VPC
6.9.3.5 Demonstration: Create a VPN connection and configure BGP in Cisco Router
6.9.3.6 Demonstration: Configure BGP route propagation in VPC
6.9.3.7 Demonstration: Delete VPN Connection, Virtual Private Gateway (vgw), Customer Gateway (cgw)
6.9.3.7.1 Demonstration: Delete VPN Connection
6.9.3.7.2 Demonstration: Delete Virtual Private Gateway (vgw)
6.9.3.7.3 Demonstration: Delete Customer Gateway (cgw)
6.10 Demonstration: Delete VPC
6.11 Miscellaneous topics in VPC
6.11.1 Traffic mirroring
7 Elastic Load Balancing (ELB) 和 Auto Scaling
7.1 Elastic Load Balancing (ELB)
7.1.1 Introduction to Elastic Load Balancing (ELB)
7.1.2 Application Load Balancer, Network Load Balancer and Gateway Load Balancer
7.1.2.1 Application Load Balancer
7.1.2.2 Network Load Balancer
7.1.2.3 Gateway Load Balancer
7.1.2.4 Comparison of different types of load balancers
7.1.3 Pricing
7.1.3.1 Application Load Balancer
7.1.3.2 Network Load Balancer
7.1.3.3 Gateway Load Balancer
7.1.4 Demonstration: Create an instance in availability zone "a"
7.1.5 Demonstration: Create an instance in availability zone "b"
7.1.6 Demonstration: Create Target Groups to "group" instances
7.1.6.1 Demonstration: Create Target Groups for availability zone "a"
7.1.6.2 Demonstration: Create Target Groups for availability zone "b"
7.1.6.3 Demonstration: Create Target Groups for availability zone "a" and "b"
7.1.7 Demonstration: Create an Application Load Balancer
7.1.8 Demonstration: Adjust path listener's rules
7.1.9 Demonstration: Verify Application Load Balancer and path listener's rules
7.1.10 Demonstration: If one target group "a" is down
7.1.11 Attach TLS / SSL Certificate in Elastic Load Balancer (ELB)
7.1.11.1 AWS Certificate Manager (ACM)
7.1.11.2 Attach to Elastic Load Balancer (ELB)
7.1.12 Demonstration: Delete Application Load Balancer
7.1.12.1 Demonstration: Delete Application Load Balancer
7.1.12.2 Demonstration: Target groups
7.1.12.3 Demonstration: Terminate instances
7.1.13 More about target group's attributes
7.1.13.1 Load balancing algorithm
7.1.13.2 Slow Start Duration
7.1.13.3 Stickiness
7.1.13.4 Deregistration delay
7.2 Auto Scaling
7.2.1 Introduction to Auto Scaling
7.2.2 Features provided by Auto Scaling
7.2.3 Launch Template
7.2.4 Auto Scaling Groups (Minimum, Maximum and Desired capacity)
7.2.5 Pricing
7.2.6 Demonstration: Auto Scaling (Manual)
7.2.6.1 Demonstration: Create an SNS notification (optional)
7.2.6.2 Demonstration: Create a Target Group
7.2.6.3 Demonstration: Create an Application Load Balancer
7.2.6.4 Demonstration: Create a Launch Template
7.2.6.5 Demonstration: Create an Auto Scaling Group
7.2.6.6 Demonstration: Exploring Scheduled Actions
7.2.6.7 Demonstration: Manual Scale Out
7.2.6.8 Demonstration: Manual Scale in to minimum capacity
7.2.6.9 Demonstration: Adjusting Scaling Policy to Auto Scaling based on CPU utilization
7.2.6.10 Demonstration: Scaling out when CPU Utilization is high
7.2.6.11 Demonstration: Delete Auto Scaling (Based on CPU Utilization)
8 Simple Storage Service (S3), Storage Gateway, Elastic File System (EFS) and FSx
8.1 Simple Storage Service (S3)
8.1.1 Introduction to S3
8.1.2 "Size" of S3
8.1.2.1 Multipart Upload
8.1.3 S3 Transfer Acceleration
8.1.4 Storage classes and pricing
8.1.5 Event Notification
8.1.6 Object Lock
8.1.7 Protecting Data Using Encryption
8.1.7.1 Server-side
8.1.7.1.1 SSE-S3 (Server-Side Encryption with Amazon S3-Managed Keys)
8.1.7.1.2 SSE-KMS (Server-Side Encryption with AWS KMS-Managed Keys)
8.1.7.1.3 Dual-layer server-side encryption with AWS KMS keys (DSSE-KMS)
8.1.7.1.4 SSE-C (Server-Side Encryption with Customer-Provided Keys)
8.1.7.2 Client-side
8.1.8 Versioning
8.1.9 Lifecycle Management
8.1.10 S3 Select (CSV or JSON)
8.1.11 S3 Batch Operations
8.1.12 Replication
8.1.12.1 Cross-Region Replication (CRR)
8.1.12.2 Same-Region Replication (SRR)
8.1.13 Requester Pays
8.1.14 Access Points
8.1.15 Special types of buckets
8.1.15.1 Directory Buckets
8.1.15.2 Table Buckets
8.1.15.3 Vector Buckets
8.1.16 Demonstration: S3 bucket and its operations
8.1.16.1 Demonstration: Create a S3 bucket
8.1.16.2 Demonstration: Upload a file to S3
8.1.16.3 Demonstration: Explore a file's properties
8.1.16.4 Demonstration: Download a file from S3
8.1.16.5 Demonstration: Exploring lifecycle rules
8.1.17 Demonstration: Versioning
8.1.18 Demonstration: Making "Public"
8.1.19 Demonstration: Delete a bucket
8.1.20 Hosting static website / contents
8.1.20.1 Demonstration: Hosting static website
8.1.21 Miscellaneous topics in Amazon S3 (MFA delete and pre-signed URL)
8.2 Storage Gateway
8.2.1 Introduction to Storage Gateway
8.2.2 Amazon S3 File Gateway
8.2.3 Amazon FSx File Gateway (May not be available for new customers
8.2.4 Volume Gateway
8.2.5 Tape Gateway
8.2.6 Storage Gateway Virtual Machine (VM) and Local cache
8.2.6.1 Storage Gateway Virtual Machine (VM)
8.2.6.1.1 Hardware and storage requirements
8.2.6.1.1.1 EC2 requirements
8.2.6.1.1.2 Storage requirements
8.2.6.2 The role of local cache
8.2.7 Demonstration: Storage File Gateway
8.2.7.1 Demonstration: NFS client
8.2.7.2 Demonstration: Create a S3 bucket
8.2.7.3 Demonstration: Creating Storage Gateway through EC2 instances
8.2.7.4 Demonstration: Connect and activate the gateway
8.2.7.8 Demonstration: Delete the whole setup
8.2.7.8.1 Demonstration: Delete "shared drive"
8.2.7.8.3 Demonstration: Delete storage gateway
8.2.7.8.4 Demonstration: Delete EC2 instances and security group
8.2.7.8.5 Demonstration: Delete S3 bucket
8.3 Amazon Elastic File System (EFS)
8.4 Amazon FSx file systems
8.4.1 Amazon FSx for Windows File Server
8.4.2 Amazon FSx for Lustre
8.4.3 Amazon FSx for OpenZFS
8.4.4 Amazon FSx for NetApp ONTAP
9 Relational Database Service (RDS), DynamoDB and ElastiCache Service
9.1 Relational Database Service (RDS)
9.1.1 Overview of data organization and Relational Database Service (RDS)
9.1.2 Introduction to Relational Database Service (RDS)
9.1.3 Multi-AZ Deployments and Read Replicas
9.1.3.1 Multi-AZ Deployments
9.1.3.2 Read Replicas
9.1.4 Auto Backup / Snapshots
9.1.5 Amazon Aurora
9.1.5.1 Aurora Endpoints
9.1.6 Demonstration: Lab Topology
9.1.7 Demonstration: Preparations
9.1.7.1 Demonstration: MySQL clients
9.1.7.2 Demonstration: Security groups
9.1.7.3 Demonstration: Subnet groups
9.1.8 Demonstration: RDS instances (Aurora, Multi-AZ, Read Replica)
9.1.8.1 Demonstration: Create the RDS cluster and instances
9.1.8.2 Demonstration: Connect RDS cluster / endpoints
9.1.9 Demonstration: Read Replica / Reader
9.1.9.1 Demonstration: Connect to the read replica
9.1.9.2 Demonstration: Create more Read Replicas / Readers
9.1.10 Demonstration: Snapshots
9.1.10.1 Demonstration: Create Snapshots
9.1.11 Demonstration: Delete RDS components
9.1.11.1 Demonstration: Delete Read Replica / Reader instances
9.1.11.2 Demonstration: Delete Master / Writer instances
9.1.11.3 Demonstration: Delete Snapshots
9.1.12 Aurora Auto Scaling
9.1.13 Aurora Serverless
9.1.14 Aurora global database
9.1.15 RDS Proxy
9.2 DynamoDB
9.2.1 Introduction to DynamoDB
9.2.2 Data model of DynamoDB
9.2.2.1 Tables
9.2.2.2 Items
9.2.3 Consistency models of DynamoDB
9.2.3.1 Eventually consistent
9.2.3.2 Strongly consistent
9.2.4 Read/Write Capacity Mode
9.2.4.1 On-Demand Mode
9.2.4.2 Provisioned Mode
9.2.4.3 Read Capacity Units (RCUs) and Write Capacity Units (WCUs)
9.2.4.3.1 RCU
9.2.4.3.2 WCU
9.2.5 DynamoDB Accelerator (DAX)
9.2.6 Table classes
9.2.7 Demonstration: DynamoDB
9.2.7.1 Demonstration: Create a DynamoDB table
9.2.7.2 Demonstration: Create DynamoDB items
9.2.7.3 Demonstration: Delete DynamoDB tables
9.3 ElastiCache
9.3.1 Introduction to ElastiCache
9.3.1.1 Redis OSS
9.3.1.2 Memcached
9.3.1.3 Redis OSS vs Memcached
9.3.1.4 Valkey Cache
9.3.2 In-memory data store
9.3.3 Use Cases for ElastiCache
9.3.4 Container and Docker
9.3.4.1 Container
9.3.4.2 Docker
9.3.4.2.1 Docker images
9.3.4.3 Demonstration: Install Docker in EC2
9.3.4.4 Demonstration: Download container / Docker images
9.3.4.5 Demonstration: Create a Redis container
9.3.4.6 Demonstration: Go to the Redis container
9.3.4.7 Demonstration: Exit and kill the container
9.3.5 Demonstration: ElastiCache Service with Redis
9.3.5.1 Demonstration: Redis clients (EC2)
9.3.5.2 Demonstration: Security groups
9.3.5.3 Demonstration: Create a Redis node
9.3.5.4 Demonstration: Connect to a Redis node and subnet group
9.3.5.5 Demonstration: Delete the Redis node
9.3.5.6 Demonstration: Delete the Redis client (EC2)
10 Route 53
10.1 Introduction to Route 53
10.2 Hosted Zone
10.3 DNS record types
10.3.1 "Standard" record types
10.3.2 "Alias" records
10.4 Time to reflect changes
10.5 DNS query logging
10.6 Health Checks & DNS Failover
10.6.1 Health Checks
10.6.2 DNS Failover
10.7 Route 53 Resolver
10.8 Demonstration: "Integrate" public hosted zone to registered domains
10.9 Routing Policies
10.10 Demonstration: Routing Policies
10.10.1 Demonstration: Routing Policy (Simple)
10.10.2 Demonstration: Routing Policy (Weight)
10.10.3 Demonstration: Routing Policy (Geolocation)
10.10.4 Demonstration: Routing Policy (Latency)
10.10.5 Demonstration: Routing Policy (Multivalue answer)
10.10.6 Demonstration: Routing Policy (IP-based)
10.10.7 Demonstration: Routing Policy (Geoproximity)
10.10.8 Demonstration: Routing Policy (Health Checks + Failover)
10.10.8.1 Demonstration: Prepare S3 static web host
10.10.8.2 Demonstration: Prepare an EC2 instance with web server
10.10.8.3 Demonstration: Routing Policy (Failover with Health Checks)
10.10.8.4 Demonstration: Routing Policy with Health Checks and Failover
10.10.8.5 Demonstration: Clean Up
10.10.8.5.1 Demonstration: Delete the record
10.10.8.5.2 Demonstration: Terminate the EC2 instance
10.10.8.5.3 Demonstration: Delete the S3 bucket
10.10.8.5.4 Delete Route 53 Health Check
11 CloudFront
11.1 Introduction to CloudFront
11.2 Edge Locations and high performance
11.3 Expiration period and Invalidation API
11.3.1 Expiration period
11.3.2 Invalidation API
11.4 Updating content
11.5 Demonstration: CloudFront
11.5.1 Demonstration: Preparation
11.5.1.1 Demonstration: Create a S3 bucket for images
11.5.1.2 Demonstration: Upload contents to S3 buckets
11.5.2 Demonstration: Create CloudFront Distribution
11.5.3 Demonstration: Verify S3 bucket policy
11.5.4 Demonstration: Clean up
11.5.4.1 Demonstration: Disable a CloudFront distribution
11.5.4.2 Demonstration: Delete a CloudFront distribution and OAI
11.5.4.3 Demonstration: Delete a S3 bucket
11.6 CloudFront cache policy
11.7 CloudFront origin request policy
11.8 CloudFront response headers policy
12 Simple Queue Service (SQS), Lambda, API Gateway and X-Ray
12.1 Simple Queue Service (SQS)
12.1.1 Introduction to SQS (Simple Queue Service)
12.1.2 Standard queues and FIFO queues
12.1.2.1 Standard queue
12.1.2.2 FIFO queue
12.1.3 Demonstration: SQS
12.1.3.1 Demonstration: Create a SQS queue
12.1.3.2 Demonstration: Send a message to the queue
12.1.3.3 Demonstration: Polling for messages / read messages
12.1.3.4 Demonstration: Delete messages
12.1.3.5 Demonstration: Delete a SQS queue
12.2 Lambda
12.2.1 Introduction to Lambda and serverless computing
12.2.2 Triggers
12.2.3 Stateless
12.2.4 Lambda@Edge / CloudFront functions
12.3 API Gateway
12.3.1 Introduction to API Gateway
12.3.2 CORS (Cross-Origin Resource Sharing)
12.3.3 API Gateway endpoints
12.3.3.1 Edge-optimized API endpoints
12.3.3.2 Regional API endpoints
12.3.3.3 Private API endpoints
12.3.4 X-Ray
12.3.5 Step Functions
12.3.6 Lambda SnapStart
12.3.7 Demonstration: Lambda (with Node.js) + API Gateway
12.3.7.1 Goal
12.3.7.2 Demonstration: Create a Lambda execution role
12.3.7.3 Demonstration: Create a Lambda function with API Gateway as a trigger
12.3.7.4 Demonstration: Create a test event and test the Lambda function
12.3.8 Demonstration: Enable X-Ray in Lambda function
12.3.9 Demonstration: Clean up
12.3.9.1 Demonstration: Delete Lambda functions
12.3.9.2 Demonstration: Delete API Gateway
12.3.9.3 Demonstration: Delete IAM roles
12.4 More about Lambda
13 Identity and Access Management (IAM)
13.1 Introduction to IAM
13.2 IAM resources
13.2.1 IAM roles
13.2.2 IAM users
13.2.3 IAM Groups / IAM User Groups
13.2.4 IAM Permissions
13.2.4.1 An example of permission
13.2.5 IAM policies
13.3 Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
13.4 Demonstration: IAM
13.4.1 Demonstration: Create a group with "administrator" permissions
13.4.2 Demonstration: Create an administrator IAM user with "administrator" group
13.4.3 Demonstration: IAM user sign-in link and perform sign-in operations
13.4.4 Demonstration: Limit EC2 operations
13.4.4.1 Demonstration: Preparation
13.4.4.1.1 Demonstration: Create an instance for testing
13.4.4.1.2 Demonstration: Remove "administrator" permissions
13.4.4.2 Demonstration: Create Policy
13.4.4.3 Demonstration: Attach policies to users
13.4.4.4 Demonstration: Verify if the policy functions properly
13.4.5 Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
13.4.6 Demonstration: Clean up
13.4.6.1 Demonstration: Delete groups
13.4.6.2 Demonstration: Delete users
13.4.6.3 Demonstration: Delete policies
13.4.6.4 Demonstration: Terminate EC2 for testing
13.5 Switch Role, Assume Role and Security Token Service (STS)
13.5.1 Switch Role and Assume Role
13.5.2 Demonstration: Switch roles, assume roles
13.5.2.1 Demonstration: Create an IAM user to assume role
13.5.2.2 Demonstration: Create an IAM role to be switched or assumed
13.5.2.3 Demonstration: Switch roles
13.5.3 Security Token Service (STS)
13.5.3.1 Demonstration: Use STS to obtain a temporary security credential
13.5.3.2 Demonstration: Delete lab resources
13.6 AWS IAM Identity Center (Successor to AWS Single Sign-On)
13.6.1.1 Identity Management Center (SSO) Configurations
13.7 Amazon Cognito
13.8 AWS Organizations and AWS Control Tower
13.8.1 AWS Organizations
13.8.2 AWS Control Tower
13.8.2.1 Landing Zone Setup
13.8.2.2 Guardrails
14 AWS Certified Solutions Architect - Associate Examination
14.1 Examination details
14.2 Examination registration
15 Miscellaneous topics
15.1 VPC peering / Peering connections
15.2 AWS Direct Connect and transit gateway
15.3 Kinesis
15.3.1 Kinesis vs SQS
15.4 Redshift
15.5 AWS Config
15.6 CloudTrail
15.7 ECS (Elastic Container Service)
15.7.1 Containers
15.7.2 Elastic Container Service (ECS) and container orchestration
15.8 Amazon EKS
15.9 Elastic Beanstalk
15.10 AWS Database Migration Service (DMS)
15.11 AWS DataSync
15.12 AWS Snowball / Snowball Edge Storage Optimized / Snowball Edge Compute Optimized
15.13 Amazon Athena
15.14 AWS Shield
15.15 AWS WAF (Web Application Firewall)
15.16 AWS Secrets Manager
15.17 AWS Systems Manager Parameter Store
15.18 Amazon Inspector
15.19 Amazon Macie
15.20 Amazon GuardDuty
15.21 Global accelerator
15.22 Compute optimizer
15.23 Cost allocation tag
15.24 AWS Backup
15.25 Amazon Rekognition
15.26 Amazon Textract
15.27 Amazon Polly
15.28 Amazon Elastic Transcoder
15.29 AWS Lake Formation and AWS Glue
15.29.1 Apache Parquet
15.29.1.1 Demonstration: Convert a csv file to Apache Parquet format by Python
15.30 Amazon EMR
15.31 Trusted Advisor
15.33 CloudFormation
15.34 Outposts
16 Further reading
16.1 EBS: From unencrypted to encrypted volume
16.2 An Integrated design of ELB, EC2, VPC Subnets, NACL and security group
16.3 AWS Auto Scaling default termination policy
16.4 CloudFront Security
16.4.1 Geo-Restriction
16.4.2 TLS / SSL (https) and custom domain name
16.4.4 More about Origin access
16.4.4.1 Public
16.4.4.2 Origin access control settings
16.5 Fault tolerance for an Aurora DB cluster
16.6 Amazon Time Sync Service
16.7 CodePipeline
16.8 AppSync
16.8.1 GraphQL
16.8.2 AppSync and GraphQL
16.8.3 GraphQL Resolvers
16.9 More about Kinesis
16.9.1 Kinesis Firehose
16.9.2 Kinesis Streams
16.9.2.1 Other types of Kinesis
16.10 DynamoDB Streams
The course content above may change at any time without notice in order to better reflect the content of the examination.
 付款。
付款。