(在家觀看 = 0%,在校觀看 = 100%)
100% 在校觀看日期及時間:
自由選擇,點選以下地區觀看辦公時間及位置
課時: 24 小時
享用時期: 8 星期。進度由您控制,可快可慢。
課堂錄影導師:Larry
在校免費試睇:首 3 小時,請致電以上地點與本中心職員預約。
本課程提供在校免費重睇及導師解答服務。
(在家觀看 = 100%,在校觀看 = 0%)
100% 在家觀看日期及時間:
每天 24 小時全天候不限次數地觀看
課時: 24 小時
享用時期: 8 星期。進度由您控制,可快可慢。
課堂錄影導師:Larry
在校免費試睇:首 3 小時,請致電以上地點與本中心職員預約。
本課程提供導師解答服務。
第五代移動網絡 ![]()
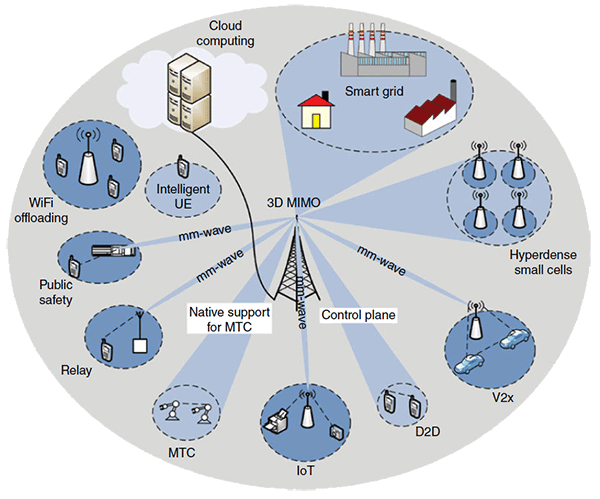
即將來臨的第五代行動通訊系統 (5G) 將如何影響您的生活?
5G 技術除了令您享受更快速的上網服務之外,還提供更多元化的服務及創新的技術!
正如十多年前雲端運算 (Cloud Computing) 的面世徹底地改革了企業運算的模式,5G 也勢必改革整個電訊行業的生態,並且普遍地影響人們的生活!
5G 為您帶來:
- Internet of Things (IoT) 物聯網 及 Smart Home 智能家居
- Vehicle-to-X (Vehicle-to-Vehicle 及 Vehicle-to-Infrastructure) 車輛之間的通訊能力及無人駕駛
- Multi-Gigabit Device-to-Device (D2D) 流動網絡
- 嶄新的家居,工業或商用的能源管理方案 (Energy Management Solution)
- 智慧電網 (Smart Grid) 及 智慧城市 (Smart City)
- 機器對機器通訊 (Machine Type Communication - MTC)
事實上在國內,已有數千 5G 發射基站完成部署並隨時可以投入生產。而各國媒體估算未來數年,中國將投入 1.2 萬億元人民幣,共部署 500 萬個 5G 發射基站,為數約等於上代 4G 發射基站的 1.5 倍。而本港於 2019年首季以先導計畫形式,開放約 1000 個適合安裝 5G 基站的政府場所。
香港商用的 5G 服務約於 2020 年面世,並於 2020 年至 2023 年期間普及。香港為此正加緊準備,包括 2020 年將指配共 4500 兆赫 (Megahertz) 的 5G 頻譜,數量是現時用於 2G、3G 及 4G 流動服務頻譜總和的 8 倍。
作為 i.t. 人的您應該如何面對新一浪科技革新的衝擊?
本課程將為您詳盡教授 5G 的無線電技術及應用場合,並教授因部署 5G 而帶來的數據中心網絡改革技術 (如 Software Defined Networking 及 Network Function Virtualization),務求幫助學員了解未來重要 5G 科技的結構原理,從而應付未來的挑戰及發掘 5G 普及帶來的商機!
| 課程名稱: |
5G 移動網絡及 SDN/NFV 網絡功能虛擬化入門課程 - 簡稱:5G Training Course |
| 課程時數: | 合共 24 小時 (共 8 堂) |
| 適合人士: | 適合任何人士 |
| 授課語言: | 以廣東話為主,輔以英語 |
| 課程筆記: | 本中心導師親自編寫英文為主筆記,而部份英文字附有中文對照。 |
| 免費重讀: | 傳統課堂學員可於課程結束後三個月內免費重看課堂錄影。 |
|
課程名稱:5G 移動網絡及 SDN/NFV 網絡功能虛擬化入門課程 - 簡稱:5G Training Course |
1. Drivers for 5G: The "Pervasive Connected World"
1.1 Introduction
1.2 Historical Trend of Wireless Communications
1.3 Evolution of LTE Technology to Beyond 4G
1.4 5G Roadmap
1.5 Ten Pillars of 5G
1.6 5G in Europe
1.7 5G in North America
1.8 5G in Asia
1.9 5G Architecture
1.10 Conclusion
2. The 5G Internet
2.1 Introduction to the 5G Internet
2.2 Internet of Things and Context-Awareness
2.3 Networking Reconfiguration and Virtualisation Support
2.4 Mobility
2.5 Quality of Service Control
2.6 Emerging Approach for Resource Over-Provisioning
2.7 Summary
3. Small Cells for 5G Mobile Networks
3.1 Introduction to Small Cells
3.2 What are Small Cells?
3.3 Capacity Limits and Achievable Gains with Densification
3.4 Mobile Data Demand
3.5 Demand vs Capacity
3.6 Small-Cell Challenges
3.7 Conclusions and Future Directions
4. Cooperation for Next Generation Wireless Networks
4.1 Introduction to Next Generation Wireless Networks
4.2 Cooperative Diversity and Relaying Strategies
4.3 PHY Layer Impact on MAC Protocol Analysis
4.4 Case Study: NCCARQ
4.5 Performance Evaluation
4.6 Conclusion
5. Mobile Clouds: Technology and Services for Future Communication Platforms
5.1 Introduction to Furture Communication Platforms
5.2 The Mobile Cloud
5.3 Mobile Cloud Enablers
5.4 Network Coding
5.5 Summary
6. Cognitive Radio for 5G Wireless Networks
6.1 Introduction to 5G Radio
6.2 Overview of Cognitive Radio Technology in 5G Wireless
6.3 Spectrum Optimisation using Cognitive Radio
6.4 Relevant Spectrum Optimisation Literature in 5G
6.5 Cognitive Radio and Carrier Aggregation
6.6 Energy-Efficient Cognitive Radio Technology
6.7 Key Requirements and Challenges for 5G Cognitive Terminals
6.8 Summary
7. The Wireless Spectrum Crunch: White Spaces for 5G
7.1 Introduction to White Spaces
7.2 Background information
7.3 TV White Space Technology
7.4 White Space Spectrum Opportunities and Challenges
7.5 TV White Space Applications
7.6 International Efforts
7.7 Role of White Spaces in 5G
7.8 Conclusion
8. Towards a Unified 5G Broadcast-Broadband Architecture
8.1 Introduction to Unified 5G Broadcast-Broadband Architecture
8.2 Background information
8.3 Challenges to Be Addressed
8.4 Candidate Network Architectures for a BC-BB Convergent Solution
8.5 The BC-BB Study: What Needs to Be Done
8.6 Conclusion
9. Security for 5G Communications
9.1 Introduction
9.2 Overview of a Potential 5G Communications System Architecture
9.3 Security Issues and Challenges in 5G Communications Systems
9.4 Summary
10. SON Evolution for 5G Mobile Networks
10.1 Introduction to SON for 5G
10.2 SON in UMTS and LTE
10.3 The Need for SON in 5G
10.4 Evolution towards Small-Cell Dominant HetNets
10.5 Conclusion
11. Green Flexible RF for 5G
11.1 Introduction Green Flexible RF
11.2 Radio System Design
11.3 Nonlinear Crosstalk in MIMO Systems
11.4 Summary
12 Conclusion and Future Outlook
12.1 Design Drivers for Next-Generation Networks
12.2 5G: A Green Inter-networking Experience
12.3 A Vision for 5G Mobile
12.4 Final Remarks
13. SDN for 5G
13.1 5G SDN Network Programmability
13.2 5G SDN Multiple Hierarchies
13.3 5G SDN Advantages
14. 5G NFV and Distributed Cloud
14.1 5G NFV and Network Slicing
14.2 Distributed Cloud applications for 5G
14.3 5G NFV Controls Virtualization
 付款。
付款。