(在家觀看 = 0%,在校觀看 = 100%)
100% 在校觀看日期及時間:
自由選擇,點選以下地區觀看辦公時間及位置
課時: 54 小時
享用時期: 18 星期。進度由您控制,可快可慢。
課堂錄影導師:Larry 和 Norman
在校免費試睇:首 3 小時,請致電以上地點與本中心職員預約。
半費重考。開始觀看最後 1 堂之 1 個月內為保障期限。請務必向本中心購買考試券。
本課程提供在校免費重睇及導師解答服務。
(在家觀看 = 100%,在校觀看 = 0%)
100% 在家觀看日期及時間:
每天 24 小時全天候不限次數地觀看
課時: 54 小時
享用時期: 18 星期。進度由您控制,可快可慢。
課堂錄影導師:Larry 和 Norman
在校免費試睇:首 3 小時,請致電以上地點與本中心職員預約。
半費重考。開始觀看最後 1 堂之 1 個月內為保障期限。請務必向本中心購買考試券。
本課程提供導師解答服務。
私有雲端 (Private Cloud) 是將雲基礎設施與軟硬體資源建立在企業防火牆內,以供機構或企業內各部門共享數據中心內的資源。私有雲端是完全為您的機構或企業而運作的雲端基礎設施,管理者也通常是您的機構或企業的全職 I.T. 管理員。
由於私有雲端資料庫能為公司儲存重要資料,再加上電腦網絡的發展蓬勃,故此有很多公司,不論大、中或小型,都紛紛為公司加上資料庫並自設私有雲端 (Private Cloud) 來獲得最佳效益及資訊安全性,以致 Microsoft 的私有雲端資料庫產品 SQL Server 2012 大受歡迎,形成市場對 Microsoft 企業自設雲端認證 (Microsoft Cloud-built Certification) 人材的強大需求,所以他們的市場價值亦相對其他行業為高。
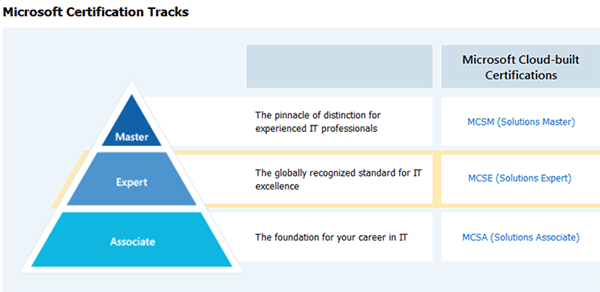
始於 2012 年雲端世代的 Microsoft 認證 : 掌握雲端運算科技,迎接未來挑戰
MCSM (Microsoft Certified Solutions Master) 可識別出位於 IT雲端業界中的「高級專家」級別人材。這些知名的高級專家至少都具有 10 年的進階 IT 業界經驗、具有 3 年或以上的實務雲端結構設計師經驗、具備健全的技術及管理技能,並且可形成一個專業菁英的社群。這個認證與其他企業認證不同,因為它是由結構設計師社群所建構,並且也是由此社群來授予的。應試者必須通過「檢閱委員會」(由先前通過認證之同級的結構設計師所組成) 的嚴格審核。該項認證的非公開培訓及考試費用高達 15.8 萬港元,考生亦必須親自前往美國接受 3 星期培訓及評審。一般來說,在位的 MCSM 都已經在美國微軟任職高級系統工程師 10 年或以上。
MCSE (Microsoft Certified Solutions Expert) 是 Microsoft 雲端世代的「專家」級國際認證考試,能證實該合格考生持有對微軟特定的解決方案具有完健的卓越技能。這些技能包括設計、專案管理、作業管理及規劃能力,而這些能力是透過其工作角色來決定的。透過驗證更為完整的技能,這些認證能夠為應試者及其僱主提供具有效力的工作效能的指標。
MCSA (Microsoft Certified Solutions Associate) 是 Microsoft 雲端世代的「夥伴」級國際認證考試,能夠讓合格考生將目標放在特定的雲端技術上,並且透過高效率地實踐企業管理層對雲端服務的適切期望,展示他們對微軟解決方案的深度的知識及獨特的專長,來突顯出自己的能力。
SQL Server 2012 的「微軟認證資料庫解決方案夥伴」(MCSA: SQL Server 2012) 能夠利用特定的指示及規格來規劃並維護資料庫。MCSA: SQL Server 2012 的合格考生擁有完整的產品知識、了解如何使用許多管理工具、效能工具、備份及回復工具等及 Transact-SQL 語言。
「資料庫解決方案夥伴」通常從事資料庫管理員、資料庫開發工程師或商業智慧開發工程師等工作,藉此展現他們豐富的技術和經驗。
 |
 |
| MCSA Logo | MCSA Certificate Sample |
| 課程名稱: |
MCSA: SQL Server 2012 (3科) 認證課程 - 簡稱:MCSA SQL Training Course (2012) |
| 課程時數: | 54 小時 (共 18 堂) |
| 適合人士: | 對電腦網絡有基本認識 及 初學數據庫人士 |
| 授課語言: | 以廣東話為主,輔以英語 |
| 課程筆記: | 本中心導師親自編寫英文為主筆記,而部份英文字附有中文對照。 |
MCSA: SQL Server 2012「微軟認證資料庫解決方案夥伴」級證書的作用是要證明你有專業水準來建立和管理 Microsoft SQL Server 2012 為本的私有雲端資料庫,而且可支援企業的實際環境與應用。是投身 IT 界人士必考的證書。而本課程的3個科目為考取 MCSA: SQL Server 2012 的必選考試科目。
| 考試編號 | 科目名稱 |
| 070-461 | Querying Microsoft SQL Server 2012 |
| 070-462 | Administering a Microsoft SQL Server 2012 Database |
| 070-463 | Implementing Data Warehouses with Microsoft SQL Server 2012 |
本中心為Microsoft指定的考試試場。報考時請致電本中心,登記欲報考之科目考試編號、考試日期及時間
(最快可即日報考)。臨考試前要出示身份證及繳付每科 HK$1,025 之考試費。
考試題目由澳洲考試中心傳送到你要應考的電腦,考試時以電腦作答。所有考試題目均為英文,而大多數的考試題目為單項及多項選擇題,其餘則為實戰題。作答完成後會立即出現合格的要求分數及你的分數,結果即考即知!
考試合格後會收到來自Microsoft的作實電郵,並進入該電郵內的連結,登入 Microsoft Credentials Dashboard 下載您的證書。
考試不合格便可重新報考,不限次數。欲知道作答時間、題目總數、合格分數等詳細考試資料,可瀏覽本中心網頁 "各科考試分數資料"。
|
課程名稱:MCSA: SQL Server 2012 (3科) 認證課程 - 簡稱:MCSA SQL Training Course (2012) |
Exam 070-461 & 070-462 Querying and Administering a Microsoft SQL Server 2012 Database (36 hours)
1. SQL Server 2012 Overview
1.1 Introduction to SQL Server 2012
1.2 Major Components of SQL Server 2012
1.3 Editions and Feature Comparisons of SQL Server 2012
2. Deploying SQL Server 2012
2.1 Windows Domain Environment
2.2 SQL Server 2012 Hardware Requirements
2.3 SQL Server 2012 Software Requirements
2.4 Installing SQL Server 2012
2. (Cont.) Network Protocols
2.1 Client – Server 2 tier SQL Networking Model
2.2 Server Network Protocols
2.3 Client Network Protocols – SQL Native Client
2.4 Choosing , Comparing SQL Network Protocols
3. Basic Concept of SQL Server Database (資料庫)
3.1 Creating SQL Server Database
3.2 Table (資料表)
3.3 Using ODBC to access SQL Server Database (請於家中進行實習)
3.6 Using OLE DB to access SQL Server 2012 Database (請於家中進行實習)
4. SQL Native Client
4.1 Deploying SQL Native Client
4.2 Connecting to SQL Sever Database by using SQL Native Client
5. Fully Qualified Names (完全合格名)
6. System Meta Data
6.1 System Databases
6.2 System Views
7. Transaction Log (交易記錄)
7.1 A Case Study of Roll Back
7.2 A Case Study of Roll Forward
8. Error Logging
8.1 Database Engine Error Severities
8.2 System Table for all error messages
8.3 Obtaining SQL Server Database Engine log
9. Alerts (警報)
9.1 Starting of SQL Server Agent
9.2 Database Mail
9.3 Setting Up an Alert Event for SQL Server Agent
10. Scheduled Jobs
10.1 Configuring Scheduled Jobs
10.2 Scripting (手稿化) Scheduled Jobs
11. Table Size
12. Index (索引)
12.1 Creating an Index
12.2 Nonclustered and Clustered Index
12.3 Non-Clustered Index with Included Columns
12.4 Using Included Columns to Avoid Size Limits
12.5 Summary of using Included Columns of a Non-clustered Index (無需強記,理解便可)
12.6 Index Usage
12.7 Fill Factor
12.8 Composite Index (組合索引)
12.9 Filtered Index
12.10 Reorganizing Index
13. Data Model
13.1 Normalization (正常化)
13.2 Cases
13.3 Relationship (關聯)
13.4 Using Normalized Database Design
14. Physical Database Architecture
14.1 Database Files
14.2 Filegroups
15. Physical Table Architecture
15.1 Table Organization
15.2 Partitioned Tables and Indexes
15.3 General Guidelines for Implementing Horizontally Partitioned Tables
15.4 Preparing a large table and Benchmarking a large table scan
15.5 Adding Extra Filegoups and Data Files
15.6 Understanding Partition Functions
15.7 Creating Partition Functions
15.8 Understanding Partition Scheme
15.9 Creating Partition Scheme
15.10 Partitioning Table Data by Datetime column
15.11 Benchmarking Partitioned Table
15.12 Guideline for Partitioned Index
15. (Cont.) Monitoring (監察) SQL Server
15.1 SQL Server Profiler
15.2 Detect Blocking
15.3 Ad hoc Blocking removal
15.4 Using Tuning Template
16. Database Engine Tuning Advisor
16.1 Introduction to Database Engine Tuning Advisor (DTA)
16.2 Using a Workload file
16.3 More references about DTA tuning options
17. Views
17.1 Understanding Standard View
17.2 Using View to provide Backward Compatibility
17.2 (Cont.) CHECK OPTION
17.3 Designing and Implementing Indexed View
17.4 Using Hints with Indexed View
17.5 Detecting Discrepancy (分歧) between Table and Indexed View
17.6 Index Statistics
18. Maintenance Plan
18.1 Transaction Information
18.2 Structural and Logical Integrity of a database
18.3 Automated Maintenance Plan
18.4 Emergency Administration
19. Resource Monitoring
19.1 About SQL Server Performance objects
19.2 Monitoring overall Memory Usage
19.2 (Cont.) Monitoring Memory used by SQL Server
20. Disaster Recovery
20.1 Three Recovery Models
20.2 Types of Backup supported in Full Recovery Model
20.3 Performing Backup
20.4 Performing Restore
20.5 Performing a Backup/Restore with SQL Server Management Studio
20.6 Information about a Backup File
21. Configuring High-Availability - Standby Server
21.1 Configuring a Standby SQL Server
22. Configuring High-Availability – Log Shipping
22.1 About Log Shipping (記錄運送)
22.2 Typical Log Shipping Configuration
22.3 Configuring Log Shipping
23. Configuring High-Availability – Database Mirroring
23.1 Database Mirroring Overview
23.2 Benefits of Database Mirroring
23.3 Configuring Database Mirroring
23.4 Connecting Clients to a Mirrored Database
23.5 Removing Database Mirroring
23.6 Combining Database Mirroring and Log Shipping
24. Configuring High-Availability – Database Replication
24.1 Elements (元素) of Replication
24.2 Choosing Suitable Replication Role
24.3 Types of Replication
24.4 Configuring Transactional Replication
24.5 Replication Performance
24.6 Comparing High – Availability Technologies (只供參考)
25. Distributed Queries
25.1 Introduction to Distributed Queries
25.2 Ad Hoc (用完即棄式) Connection
25.2 (Cont.) Linked Servers
25.3 Configuring a Linked Server Mapped Login
25.4 Pass-through Query
26. Transact-SQL
26.1 Creating a New Database
26.2 Updating Records from Another Table
26.3 Aggregate (合成) Functions
26.4 Group By
26.5 HAVING
26.6 TOP (請於家中進行實習)
26.7 DISTINCT
26.8 COALESCE (聯合產生)
26.9 CONVERT
26.10 LTRIM and RTRIM
27. Triggers (觸發裝置)
27.1 Creating a Simple Trigger
27.2 Disabling a Trigger
27.3 Creating a Trigger to Perform Verification (核對)
27.4 Creating a Trigger to Backup Modified Data
27.5 Creating a Trigger to Examine New Data
27.6 Creating a Trigger to Perform Update on Other Table
27.7 INSTEAD OF (取而代之) TRIGGER
27.8 Summary of AFTER TRIGGER v.s. INSTEAD OF TRIGGER
28. Stored Procedure
28.1 Introduction to Stored Procedure
28.2 Using Parameters (參數) in Stored Procedures
28.3 Error Handling with “TRY and CATCH”
Exam 070-463:
Data Warehouse (18 hours)
1. Design and Implement a Data Warehouse
1.1 Introduction to Data WareHouse
1.2 Elements in a Data WareHouse Solution
1.3 Data WareHouse Basic Design
1.4 Characteristics of Fact Tables
1.4.1 Granuality
1.4.2 Measures
1.4.3 Primary Key
1.4.4 Indexes
1.4.5 Columnstore Indexes
1.4.6 Partitioning
1.5 Characteristics of Dimension Table
1.5.1 Primary Key
1.5.2 Indexes
1.5.3 Conformed Dimensions
1.5.4 Time Dimension Table
2. Configuring Data Flow in SSIS
2.1 Introduction to SSIS
2.2 Data Sources
2.3 Data Destination
2.4 Connection Manager
2.5 Data Transformation
2.5.1 Exercise for Using Sort and Merge Join Transformation
2.5.2 Exercise for Using Lookup Transformation
2.5.3 Exercise for Using Derived Column and Fuzzy Lookup Transformation
2.5.4 Exercise for Using Data Conversion and Conditional Split Transformations
2.5.5 Exercise for Using Merge and Union All Transformations
2.5.6 Exercise for Deduplication Using Sort and Fuzzy Grouping Transformation
2.5.7 Exercise for Slowly Chaning Dimension Transformation
2.6 Debugging Data Flow and Handling Error Output
3. Configuring Control Flow in SSIS
3.1 Introduction to Control Flow
3.1.1 Control Flow Tasks
3.1.2 Precedence Constraints
3.2 Variables, Parameters and Expression
3.2.1 Using Variables
3.2.2 Using Parameters
3.2.3 Using Expressions
3.3 Debugging and Error Handling
3.3.1 Package Events
3.3.2 Using Data Viewer and Breakpoint
3.3.3 Logging File and Dump File
3.3.4 Handling Errors
3.4 Checkpoint and Transaction
3.4.1 Configuring Failure Behavior
3.4.2 Using Transactions
4. SSIS Deployment
4.1 Execution of SSIS Projects and Packages
4.2 Deployment Model
4.2.1 Package Deployment Model
4.2.2 Project Deployment Model
4.3 SSIS Catalog
4.3.1 Folders
4.3.2 Enviroments and Enviroment Variables
4.3.3 Operation Log and Project Versions
4.4 SQL Server Agent
5. Data Quality Services and Master Data Services
5.1 Data Quality Services (DQS)
5.1.1 Introduction to DQS
5.1.2 DQS Knowledge Base and Domains
5.1.3 Data Quality Projects
5.1.4 DQS Cleansing Transformation
5.2 Introduction to Master Data Services (MDS)
5.2.1 Setting up MDS Database
5.2.2 MDS Model and its Objects
5.2.3 MDS Data Quality Features
5.2.4 MDS Functions
5.2.5 MDS Example
 付款。
付款。